David Baker has been involved with the USA since childhood. First attending a US school in England and then studying in the US under a scholarship program sponsored by Senator Clinton P Anderson. He returned to the USA and worked for NASA on various programs from Gemini to the SpaceShuttle. He was present in mission control in 1970 and witnessed the drama of Apollo 13 first hand.
He joined the British Interplanetary Society in 1965, published his first article in the society’s journal Spaceflight in 1969 and since 2011 has been the editor of that very journal -Spaceflight. To date, he has published a remarkable 110 books by the close of 2018 with a few more in the pipeline for 2019 to mark the fiftieth anniversary of Apollo 11.
(Note – following questions on the veracity of his Phd, David Baker resigned from the BIS as the editor of Spaceflight on 25th March 2021.)
In this episode, we talk about the current status of the space programme in the US and the changing role of NASA.
- The USA has not been able to launch US astronauts from the USA since the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011. NASA found itself in a similar position between 1975 (Apollo Soyuz Test programme) and the first Space Shuttle in 1981.
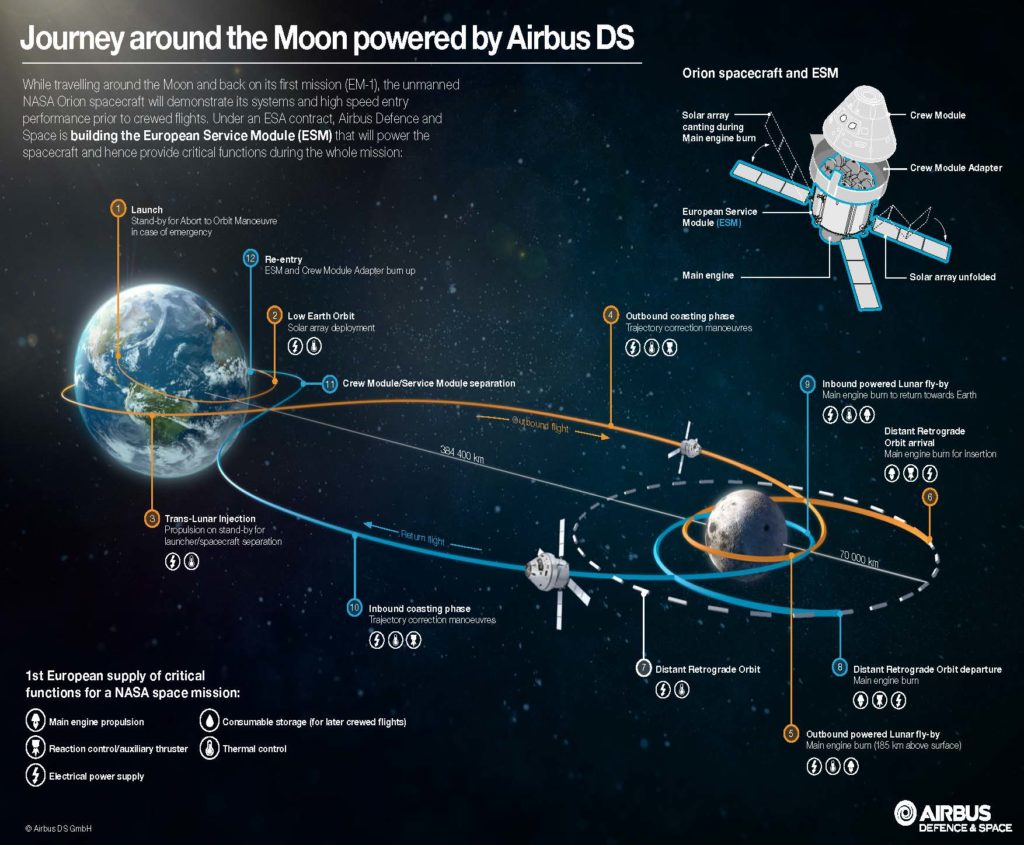
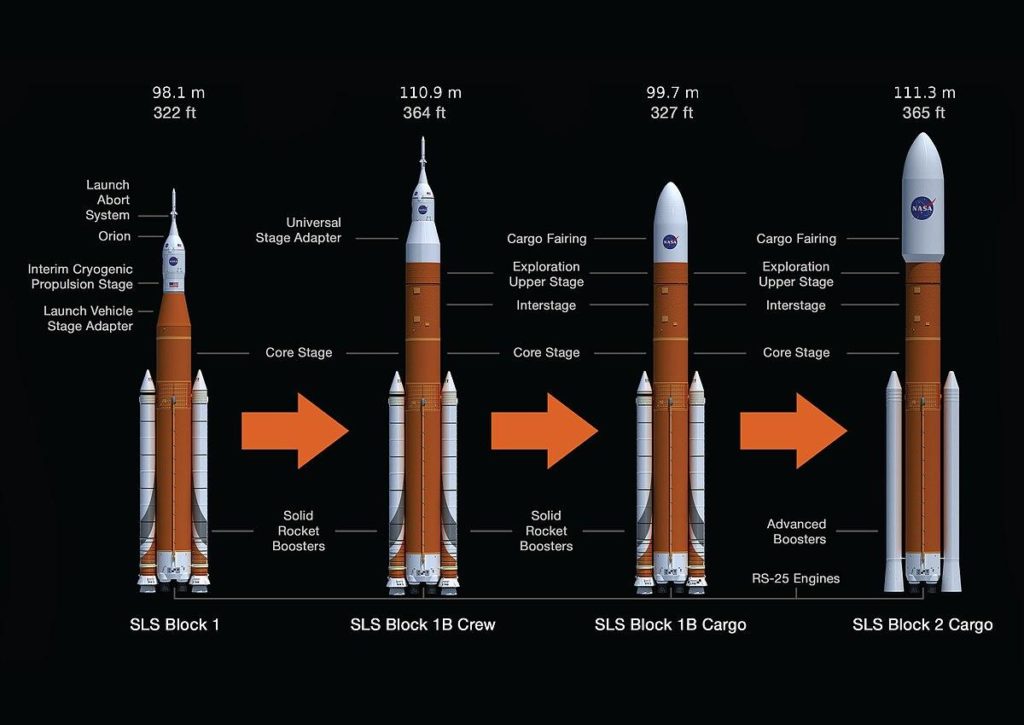
- Why NASA dropped the Ares programme and why its replacement, the Space Launch System (SLS) schedule remains unclear. The first SLS mission, uncrewed – Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) by 2020 and the second crewed mission, Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2) by 2023.
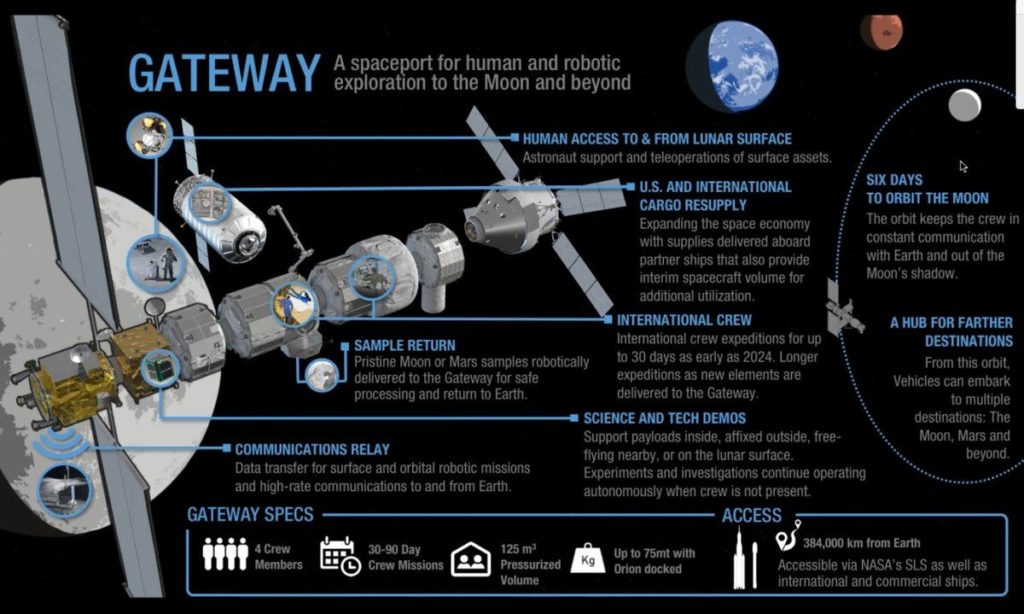
- The successor to the ISS, the “Gateway” is an international project for a space station in lunar orbit. Only about a third of the size of the ISS and it will have fewer international partners.
- The gateway is seen by Russia as an American lead programme. Will Russia participate with the gateway or consider a joint Russia/China human spaceflight programme?
- China/USA cooperation in space has been prohibited
ny US law. What prospects that this will change?

Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 30:55 — 24.8MB) | Embed
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | Spotify | RSS | More


