How many rockets were launched from Earth in 2024? From which countries and which spaceports? What rocket types were involved, and what was carried into space to which orbit?
This and much more is recorded every year by many companies, governments and organisations. However, individuals also record it in meticulous detail throughout the year and have been doing it for many years. I want to mention just two here.


Dr Jonathan McDowell (on Bluesky) is an academic from the Harvard-Smithsonian Centre for Astrophysics. Every year, he produces Jonathan’s Space Report, a downloadable (pdf). He has a list going back to 1998.

The 2024 report is just over 100 pages and full of metrics and graphs detailing the global space launches to Earth orbit and beyond. One sentence caught my eye in this year’s report. It was a reference to a launch not from the Earth but to the Earth. On page 4, referring to launches he did not include in his data, he says, “excluded is 2024-U02, a Chinese launch from the surface of the Moon.” This was the Chang’e-6 lunar sample return mission. A casual statement capturing the “routineness” of humanity’s current space capabilities.
Jonathan’s Space report covers an incredible amount of data that answers the questions I outlined in the first paragraph. Incredible, that he does all this on the side of his day job as an astrophysicist.
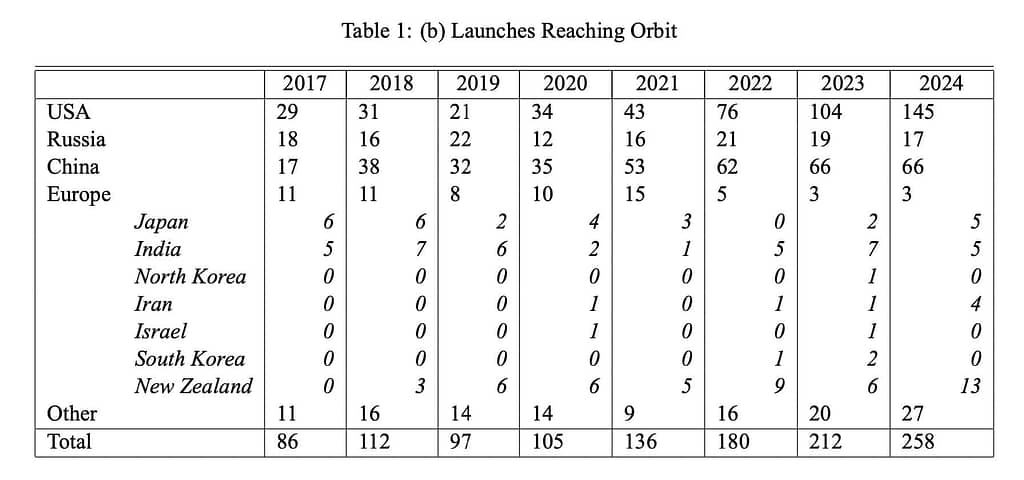
Jonathan’s summary includes a comparison of successful launches in 2024 going back to 2017. It captures the increasing launch cadence for the USA and China. The delayed introduction by ESA of Ariane 6 has held back launches in Europe.
Anatoly Zak (on bluesky) is a journalist originally from Moscow and has now been based in the USA for over three decades. He has written for many publications and books but is best known for his dynamic website, russianspaceweb.com. His summary of space launches for 2024 is available here: www.russianspaceweb.com/2024.html, as are similar summaries for previous years (change the year in the URL).
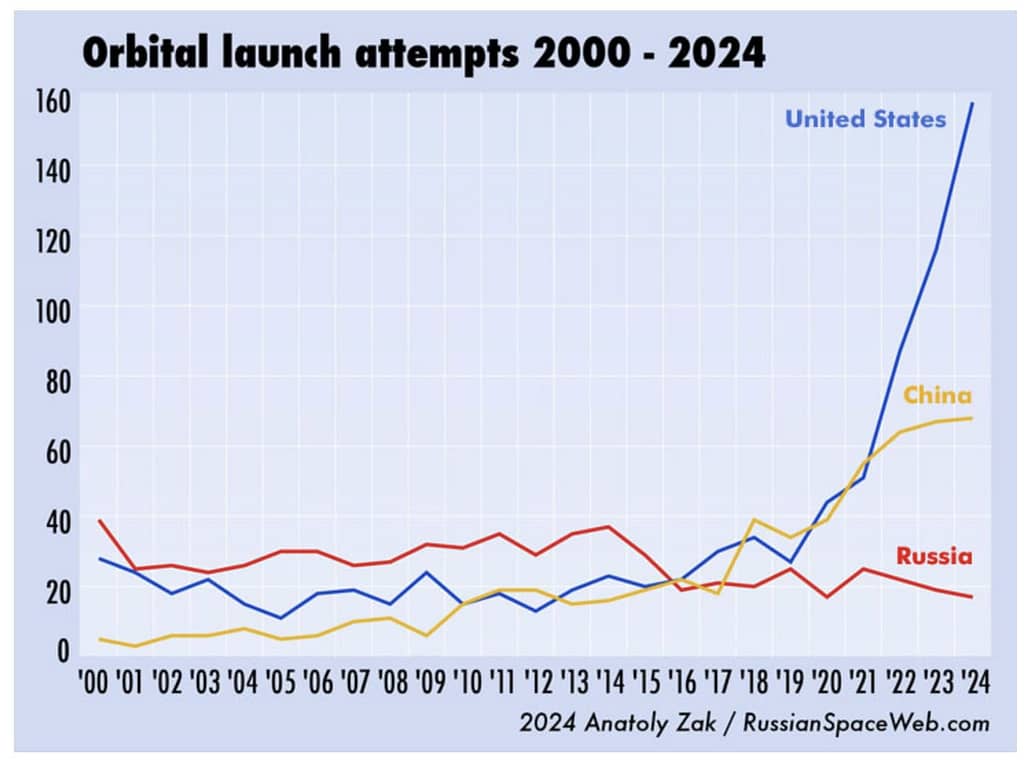
Anatoly Zak lists all the detailed metrics for 2024 and captures this dramatic rise in launches with a single graphic.
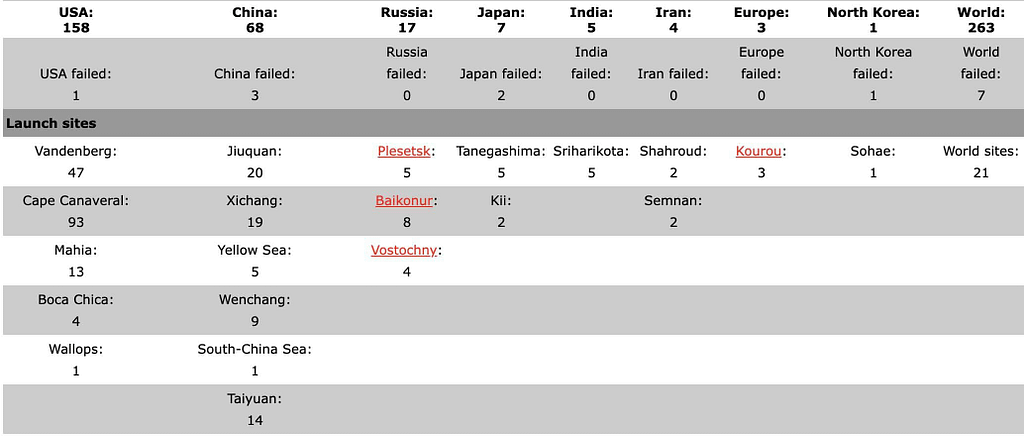
For 2024, the global launch statistics show that the USA remains the leader with 158 launches and China second with 68. More countries and companies are developing their own large constellations for space-based internet access, global GPS systems, communication, and Earth Observation. In addition, 2025 is expected to be busy with an unprecedented two dozen missions to the Moon.