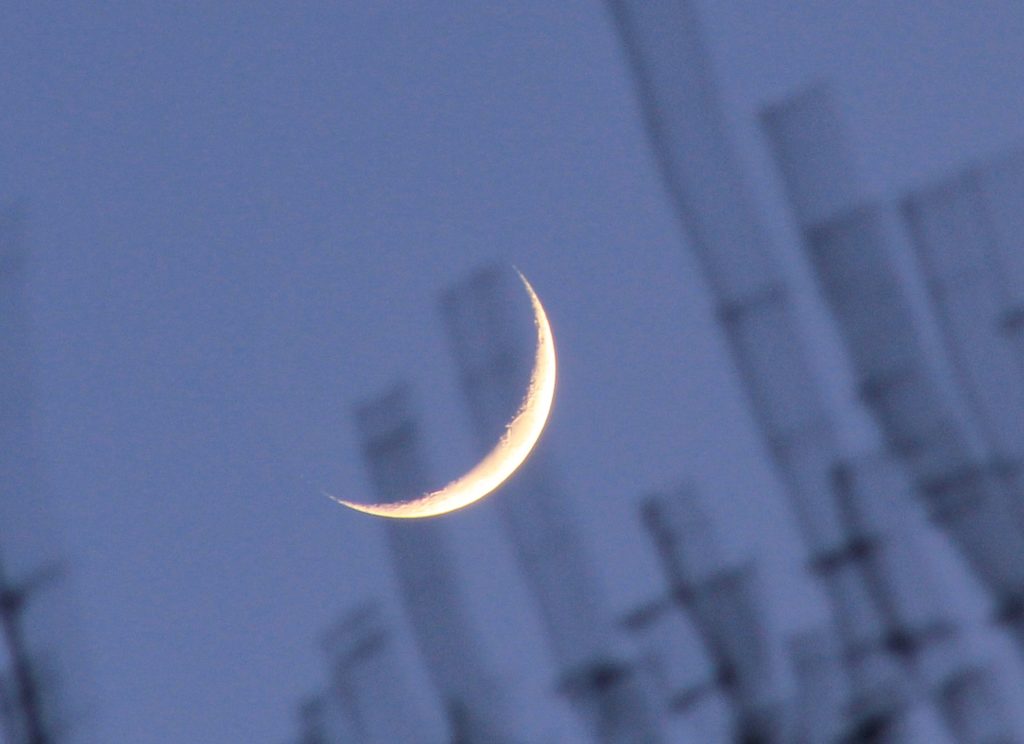
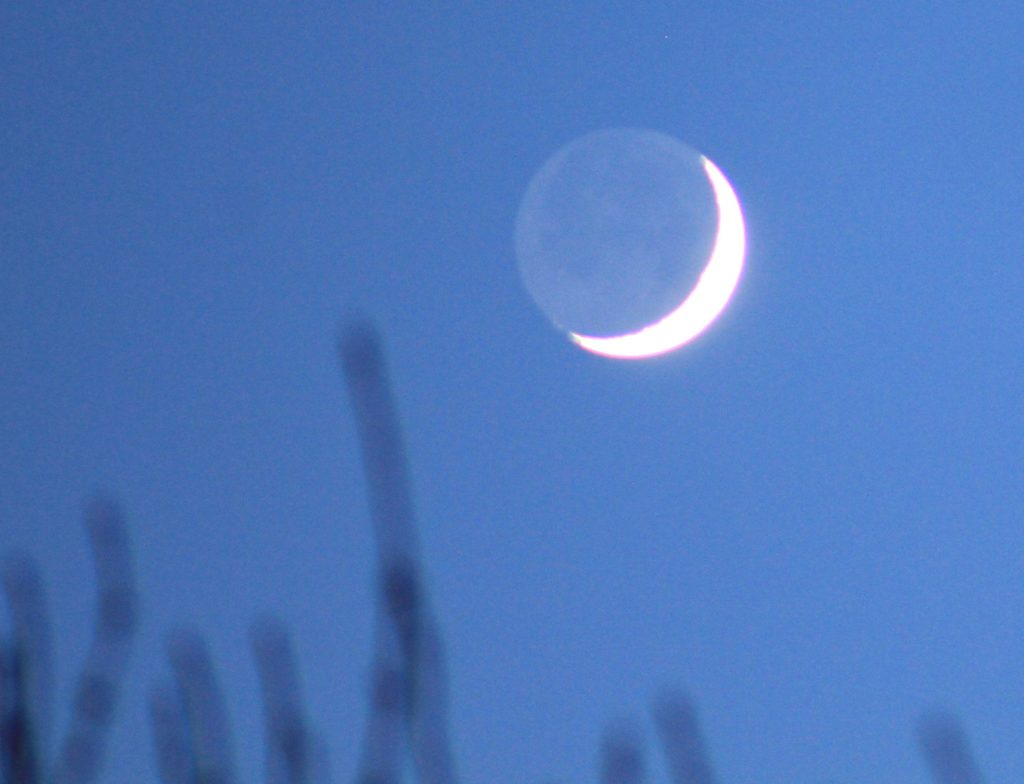
ISS over Manchester

A brief silver lining during the nation-wide Covid-19 lock-down. A few days of cloud-free sunny weather coinciding with a flyby of the International Space Station over northern England.
For more ISS passes, other spacecraft and in your location see – https://www.heavens-above.com/
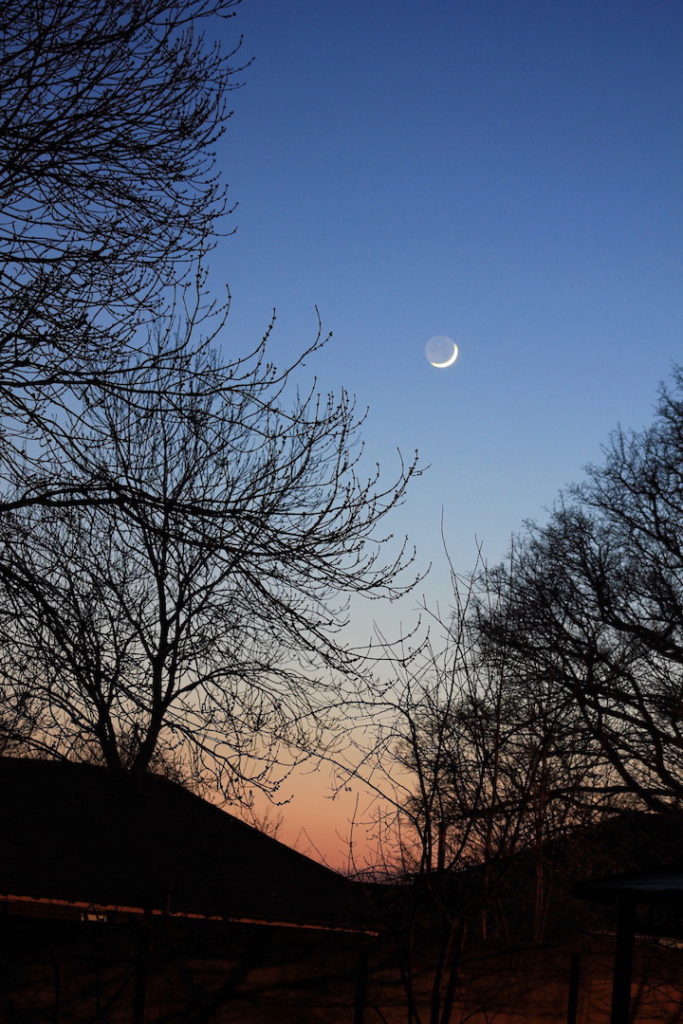

Earthshine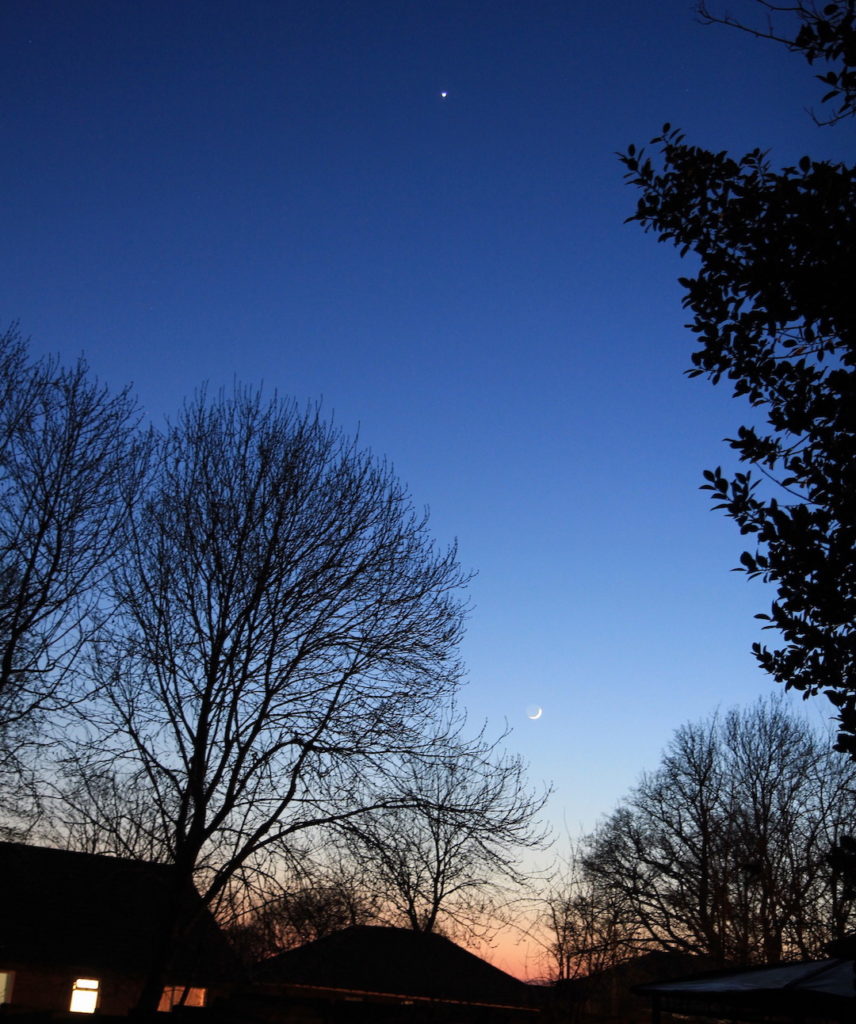 
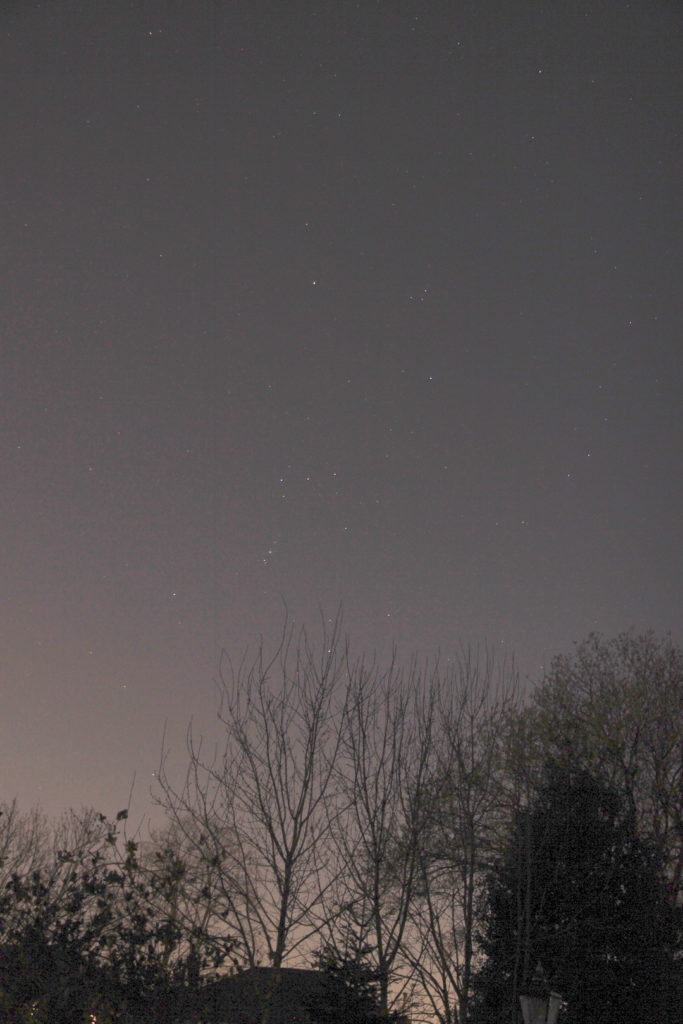

Orion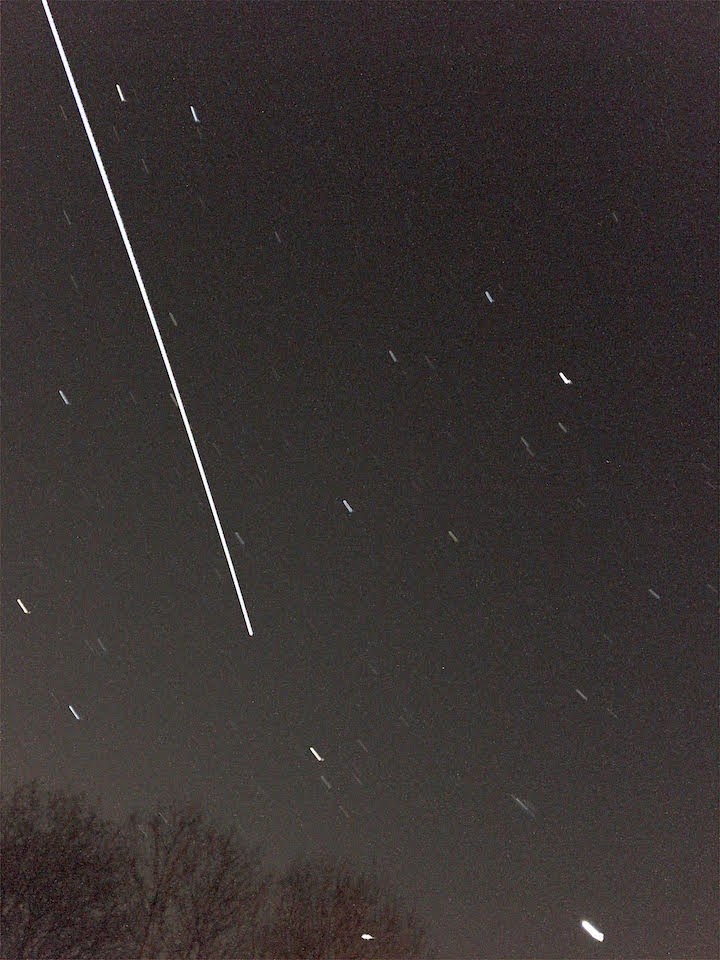 
ISS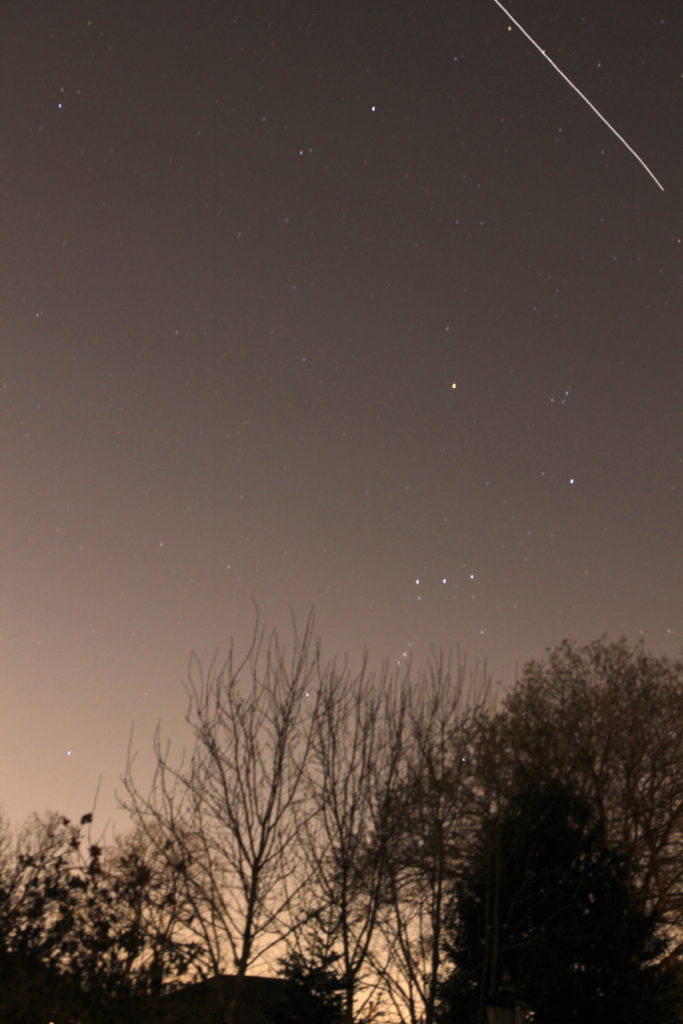 
ISS rising over Orion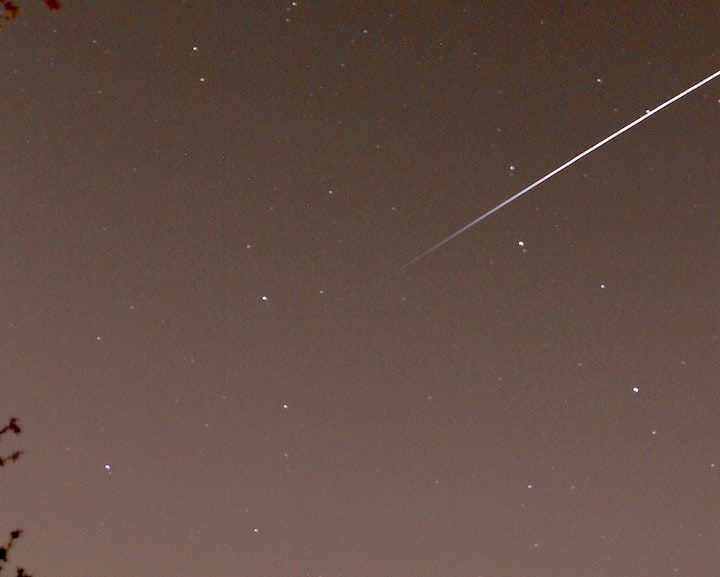 
ISS passing throgh the zenith and in to Earth’s shadow
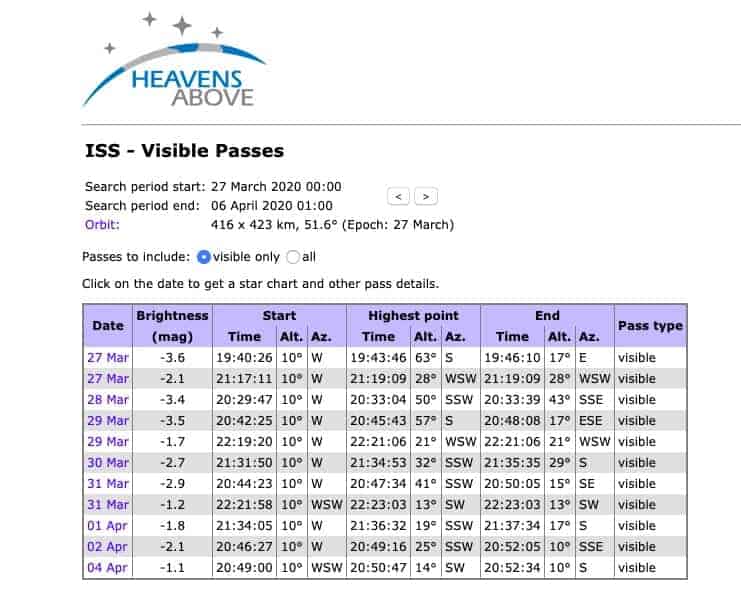
For the next few days for the UK it looks like this. For other spacecraft and for your area – wherever that may be in the world, check out https://www.heavens-above.com/
Stephen Smith and Leslie Johnson. Development of rockets during the 1930s and letters from Calcutta to Liverpool

I came across the Liverpool/Calcutta connection during my research into the life and work of Stephen H Smith. During 1934 and 1944, Smith undertook around 300 rocket experiments to demonstrate the utility of a rocket to transport mail, medicines, food and living creatures. Similar experiments were being conducted in Germany, Austria, Netherlands and the USA, but in India, for over a decade it was just Smith.
The British Interplanetary Society had been founded in Liverpool in 1933. Smith conducted his first rocket experiments in September 1934 and it was published in the BIS Bulletin in November 1934. Smith in Calcutta joined the BIS around this time and established regular correspondence with the Leslie Johnson, the BIS secretary, in Liverpool. Johnson’s daughter still has a file of letters Smith sent from Calcutta to Liverpool in the late 1930s.
My book (India’s Forgotten Rocket Pioneer) will be published by the end of March 2020 and contains many pictures of Smith, his rockets and quotes from his letters. Some from the Johnson collection but other sources too.I could not include many in the book – so I am sharing some more here. Click on any of the images below to open the gallery viewer.

Smith conducted his first rocket mail experiment on 30 September 1934. It appeared in the November 1934 issue of the BIS Bulletin.
Credit National Air and Space Museum. Washington DC
In the early 1930s, the founders of nascent rocketry societies (Phil Cleator of the BIS in UK and Edward Pendray of the AIS in USA) were swapping notes on the work on rocketry being conducted by Smith and Goddard. Goddard’s contribution was incomparable to that of Smith’s.
3 April 1936 From Phil Cleater to Edward Pendray. Credit National Air and Space Museum. Washington DC

To help raise funds and raise the BIS profile, members could purchase BIS headed paper to use as “Member’s correspondence”. Smith used it widely especially when communicating with the media to assert his credentials. He also used it to write one of his many letters to Leslie Johnson in Liverpool.
29 September 1937 Members Correspondence with BIS logo. Credit Leslie Johnson
Stephen Smith (sitting bottom left) in Calcutta with a mostly obscured rocket launch frame for his rockets behind him.
22 July 1938. Credit Ramu M Srinivasa
Soon after the BIS was founded in Liverpool, the Manchester Interplanetary Society was established in nearby Manchester. Headed by Eric Burgess, it did not last long and was later subsumed in to the BIS when it was reformed after the World War II in London. The MIS was just as ambitius as the BIS and published a journal called The Astronaut.
August 1938 – Manchester Interplanetary Society’s journal – The Astronaut. Credit National Air and Space Museum. Washington DC.
7 November 1949. Stephen Smith to Robert Paganini. Transcript below.
“You may mention that I have been working on these tests for over 12 years and that my work and experiments were increasingly more and (more) until the war when the military wrote to me on numerous occasions for aid. Tell him that I was India’s Pioneer Rocket experimenter and that I am an Indian by birth, having been born in Shillong, Assam. You may mention that I have done work in the Himalayas and that my efforts have been recognised in the USA and the whole of Europe and yet I’m the land of my birth I am ignored and last though not least, thousands of my rocket mail letters, cards and stamps are scattered around the world. If his excellency the governor, Dr Katju should be interested he should send for me for a private discussion on a field of experiments now occupying the world. Thank you my good friend, thank you a thousand times and god bless you for your great kindness to me.”
7 November 1949. Credit Robert Paganini collection. Museum of Communication, Bern Switzerland.
2 March 1950 From Stephen Smith to Robert Paganini
Smith complaining that he has not received a response from any senior politicians including Prime Minister Nehru. “I have not heard a line from H.E. Dr Katju or Dr B. L Roy or Pandit Nehru. They will not have anything to do with anyone, except one who is an India. This is life.”
2 March 1950 Credit Robert Paganini collection. Museum of Communication, Bern Switzerland.
Smith hints at an “offer of his services” but cannot tell anyone.
6 April 1946 from Stephen Smith to Robert Paganini. Credit Robert Paganini collection. Museum of Communication, Bern Switzerland
Extract from Robert Paganini’s will. Paganini died on 6 December 1950. He left a quarter of his estate to Stephen Smith – someone he had never met. Smith himself died three months later.
Credit Robert Paganini collection. Museum of Communication, Bern Switzerland.
Online Course – The New Space Age
A new online introductory (yes – for beginners) course from the Workers’ Educational Association supported by the Royal Astronomical Society. Enrolment requirements include:
- You have been resident in the UK, EU or EEA for the last 3 years
- You are aged 19 years or older on 1st September 2019
- Starts at 19:00 on Tuesday 10th March 2020. Cost is £20 or free if eligible

Over six weekly ninety-minute sessions online, the course will look at space programmes and missions being conducted by many countries and companies right now. Starting 10th March 2020. The six sessions will cover
- From the Space Race to the New Space Age. How has human space exploration evolved since the launch of Sputnik in 1957?
- Services from space. All those satellites in space, what impact do they have on the quality of lives of people on Earth?
- The Private Space Sector. It has been emerging for many years. Has it finally arrived?
- Environmental control in space. Can the international community apply the lessons of climate change on Earth to the space environment around Earth and beyond?
- Militarisation of space. Humans on Earth have always fought on the land, sea and the air. Is war in space inevitable?
- Humans in Space. In this decade, will humans walk on the Moon again? Will this decade deliver, finally the promise of space tourism?



