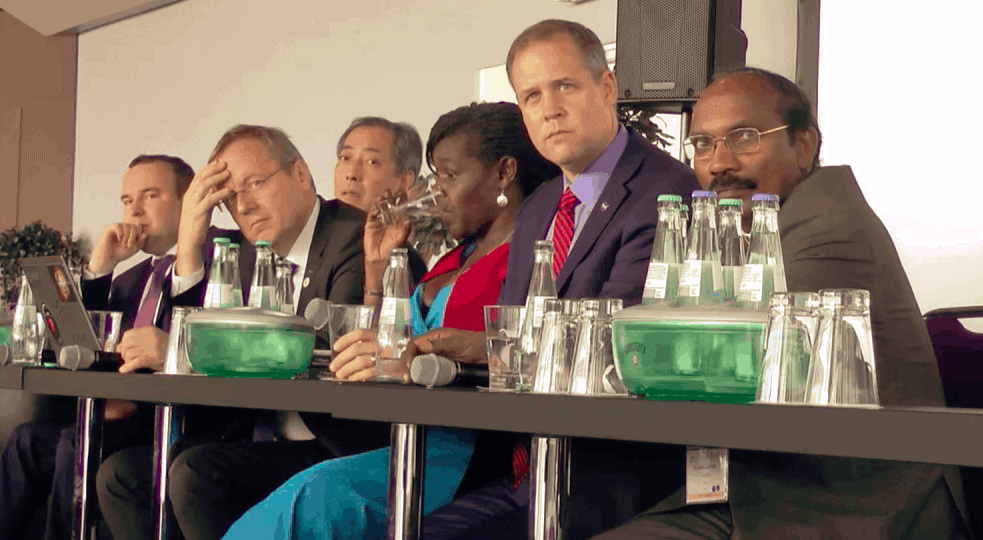
This is my recording of the Heads of Space Agency press conference, 1st October – the first day of IAC2018. This video was not initially intended to be published. But here it is
In Attendance:Left to right
- Dmitry Loskutov in place of Dmitry Rogozin – (Roscosmos)
- Hiroshi Yamakawa – (JAXA)
- Johann-Dietrich Woerner – (ESA)
- Maggie Aderin-Pocock (Moderator – BBC)
- Jim Bridenstine – (NASA)
- K. Sivan – (ISRO)
- Sylvain Laporte – Canadian Space Agency (not present)
- Zhang Kejian, China National Space Administration (not present)
Some notes
Head of Roscosmos Dmitry Rogozin – prevented by sanctions against Russia to travel to Germany. Replaced by Dmitry Loskutov.
Bridenstein:
- Experiments on ISS from 103 countries
- Gateway – Open architecture, a fraction of the size of the ISS is not in LEO so has no radiation protection from the Van Allen Belts
- Reduced electromagnetic radiation from Earth. May allow new experiments in astrophysics
- Multiple trips to the lunar surface from the Gateway and hence
potential for new science experiments on the surface. - Question: Is NASA subsidising SpaceX? Did not deny it outright at the outset.
- NASA’s goal is to establish a capability, reduce costs, and enhance innovation. Ultimately, more customers for SpaceX, not just NASA, and more service providers – not just SpaceX.
- My question is: when will the US law prohibiting US/China collaboration in space end?
- Answer: The law expires and is renewed every year. (Left it
open ended really). - Question: Is China’s space programme too close to the Chinese military? Answer: This is a concern for US government, and NASA will do what its government permits it to do
Sivan
- Indi
a has no plans for human missions to the Moon. - Regarding India cooperating with China on human spaceflight training, he left it open-ended. I think he was aware of the deal that the Modi administration was making with Russia (announced a few days later), but could not say anything at this press conference.
Woerner:
- ESA Astronauts are learning Chinese. Will fly with China in the future but no date yet.