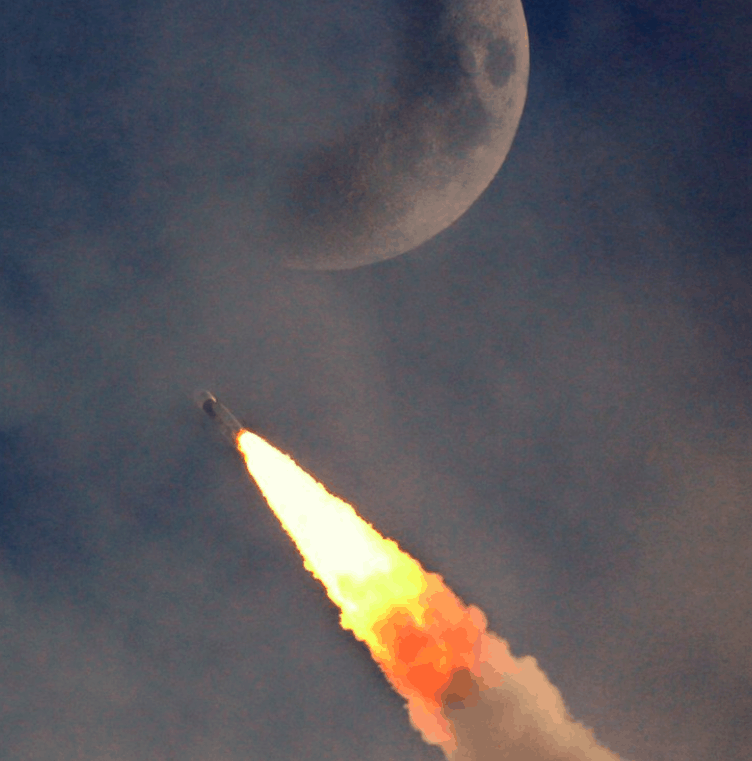

Credit: ISRO
On Wednesday 14th November 2018, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully placed a 3.4-ton communication satellite GSAT-29 in orbit with the third launch (and the second developmental flight) of its heavy launch vehicle – GSLV-Mk3. This is a huge milestone for ISRO.
This mission was critical for ISRO. Had it not been successful the impact would have had profound on it is immediate and near-term plans. In addition to taking a huge financial hit and loss of morale within the organisation, there would have been additional consequences.
- ISRO has been building and launching satellites for almost 3 decades. But operational launchers (PSLV and GSLV-MK2) do not have the capacity to launch heavy (more than 2.5 tons) satellites. So has outsourced those launches to the European Space Agency’s Ariane launcher. The successful launch of GSLV-Mk3 D2 mission means that India need not continue to rely on EAS’s Araian.
- A mission review earlier this year increased the mass of ISRO’s Lunar Lander mission Chandrayaan-2. The increased mass is beyond the capacity of a PSLV or a GSLV MK2. The Chandrayaan-2 mission is scheduled for launch in January next year. Without this success, this key mission to the Moon would have been delayed indefinitely.
- Another casualty could have been the 2022 timeline for the recently announced Human Spaceflight programme, Gaganyaan. In August, India’s Prime Minister announced India to launch a crewed spaceflight from India by 2022.
As a result of this mission, the GSLV MK3 will move from development (with D prefix) to an operational phase (with a C for continuous prefix) from 2019.
Geosynchronous Satellite (GSAT-29) is a communication satellite that will provide high-resolution imagery, radio and digital communication for northern parts of India. Designed to operate for 10 years, the ISRO chairman announced that the launch was so precise, the extra fuel will extend the satellites lifetime to at least 12 years. In the near future, GSAT-29 will be joined by two more similar satellites to support the “Digital India” programme. A more detailed report of GSLV-Mk3-D@ mission from William Graham on Nasaspacflight.com
Credit: ISRO 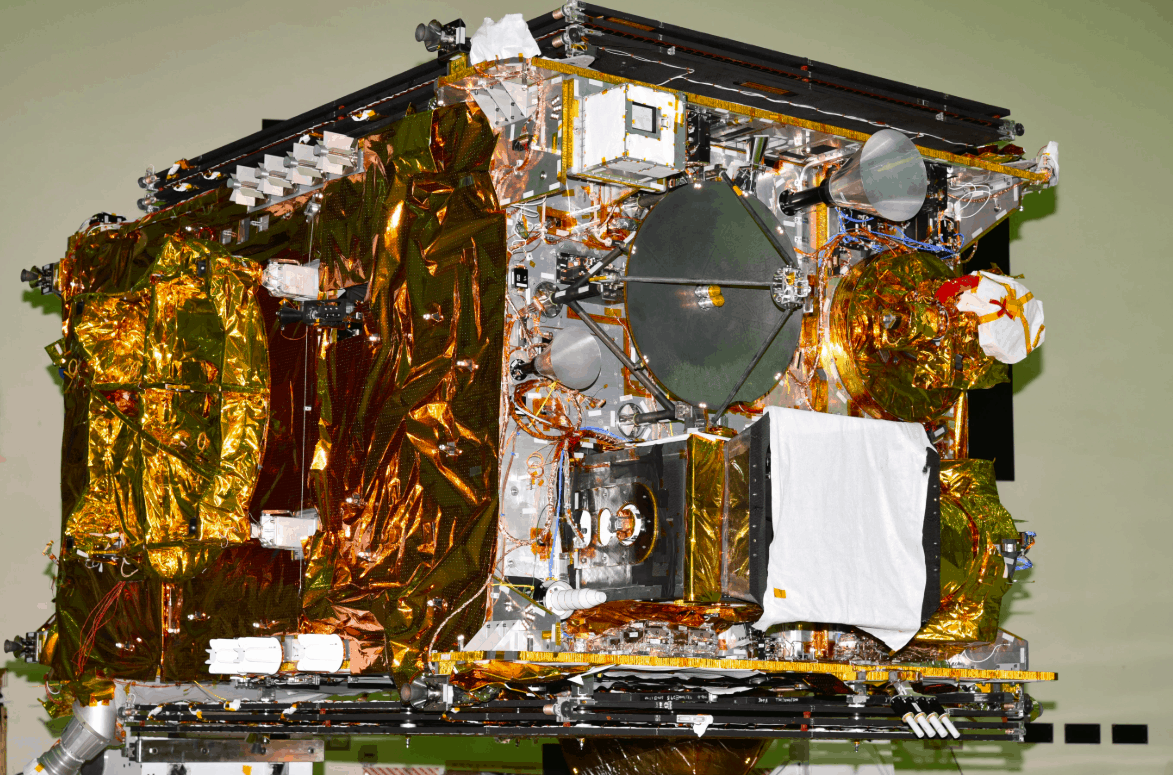
Credit: ISRO 
Credit: ISRO 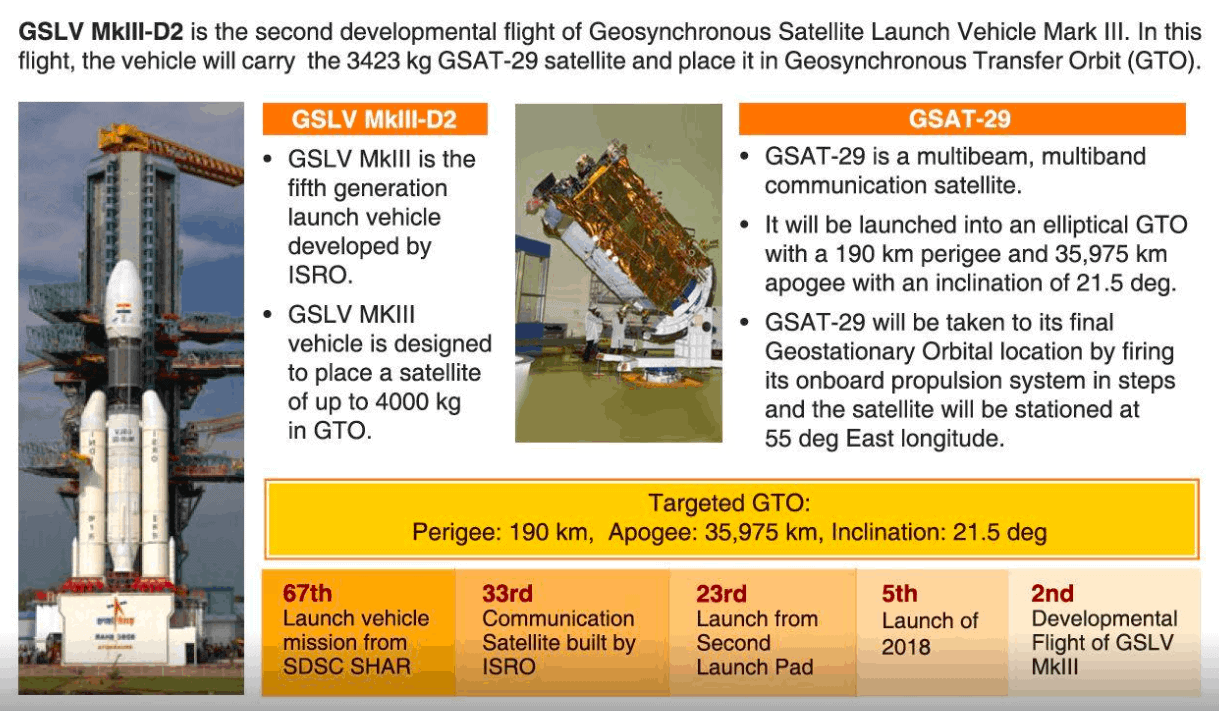
Credit: ISRO 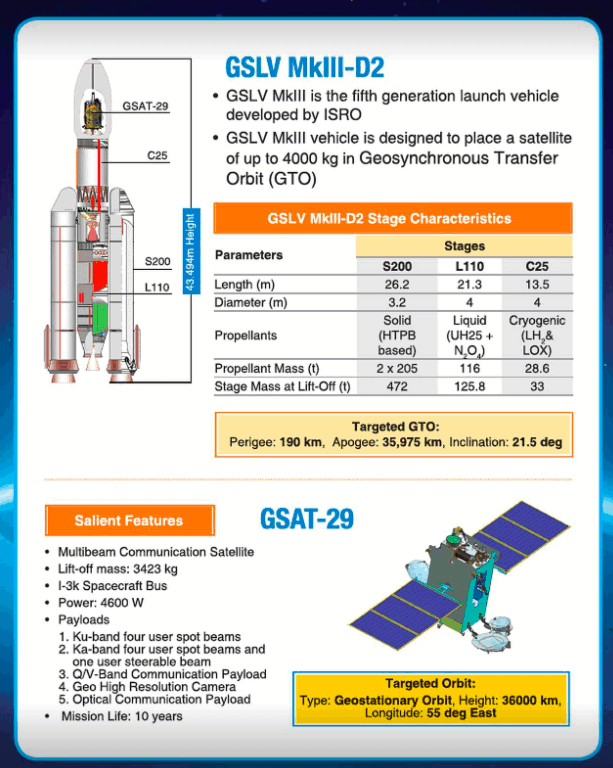
Credit: ISRO
If you missed the live stream of the pre-launch, launch and post-launch commentary – its here (all 90 minutes) on youtube.