In his 1979 novel, Fountains of Paradise, Arthur C Clarke imagines a cable stretching from the Earth’s equator to Geosynchronous orbit. He called it a “space elevator” and imagined it would be constructed from continuous pseudo-one-dimensional diamond crystals. Bangalore based NoPo Technologies is now commercially producing Carbon Nanotubes. Could this material, one day be used to construct Clarke’s space elevator?
Materials that offer high strength alongside low mass are highly sought after by the aerospace industry. In the past, it was aluminium, titanium and Carbon fibre. The new wave of materials consists of Graphene and Carbon nanotubes. Carbon nanotubes like diamonds, soot and graphene are allotropes of Carbon. Same atomic structure but differ in physical construction.
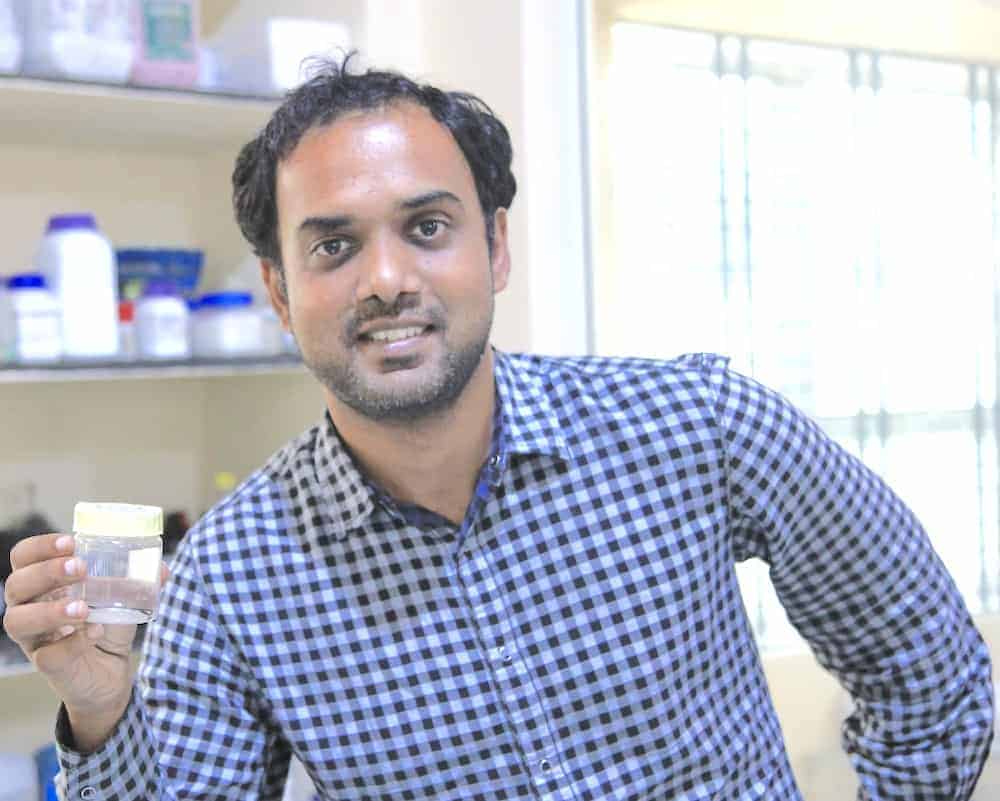
NoPo Technologies was established in 2011 by the CEO Gadhadar Reddy and is already commercially supply Carbon Nanotubes to Japan and elsewhere.
Some of the themes we discussed include:
- NoPo Technologies was incorporated in 2011 and is probably the only producer of Carbon Nanotubes in India at the present.
- Carbon Nanotubes have desirable attributes of high thermal and electrical conductivity, tensile strength, resilience to radiation and are extremely lightweight.
- Nopo Technologies commercially produce single-walled Carbon Nanotubes of about 8 nm diameter and 2000 nm long.
- Use cases currently include lightning conductors on aircraft, insulators for cryogenic fuel tanks, black surfaces for star trackers on spacecraft and molecular scale filters that can be used for producing biological membranes or even water filters for desalination plants.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 42:58 — 34.6MB) | Embed
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | Spotify | RSS | More
NOPO Offices in Bangalore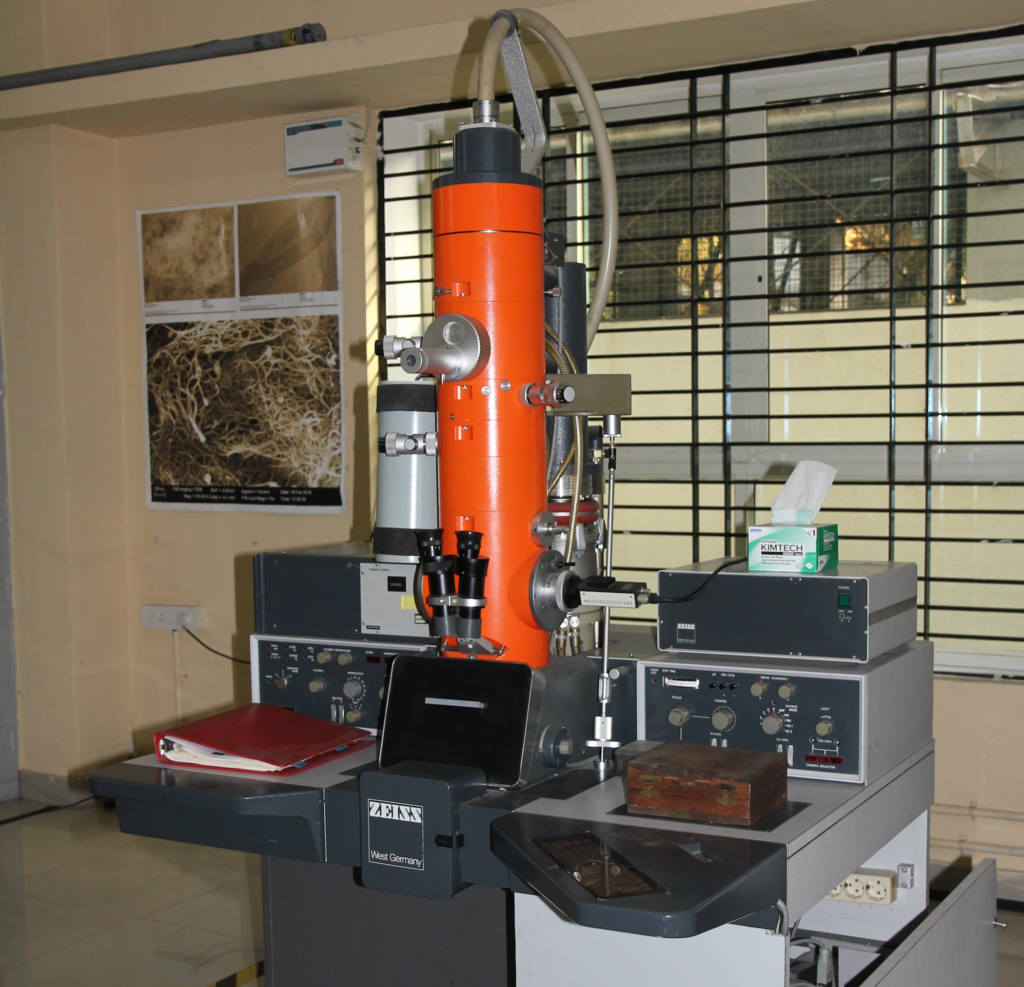 
Electron Microscope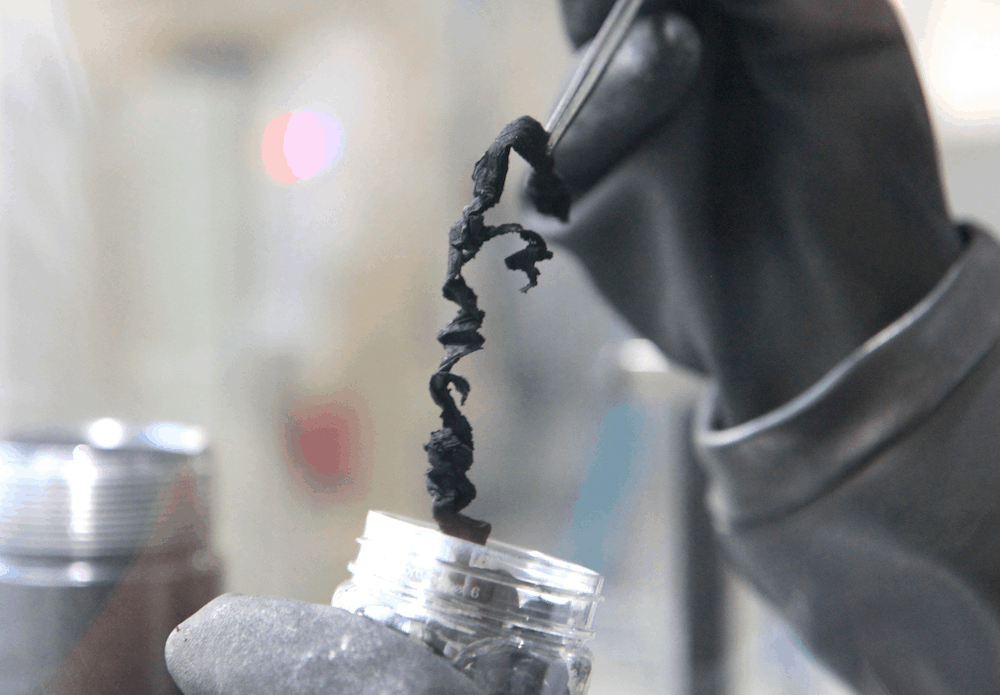 
Carbon Nanotubes 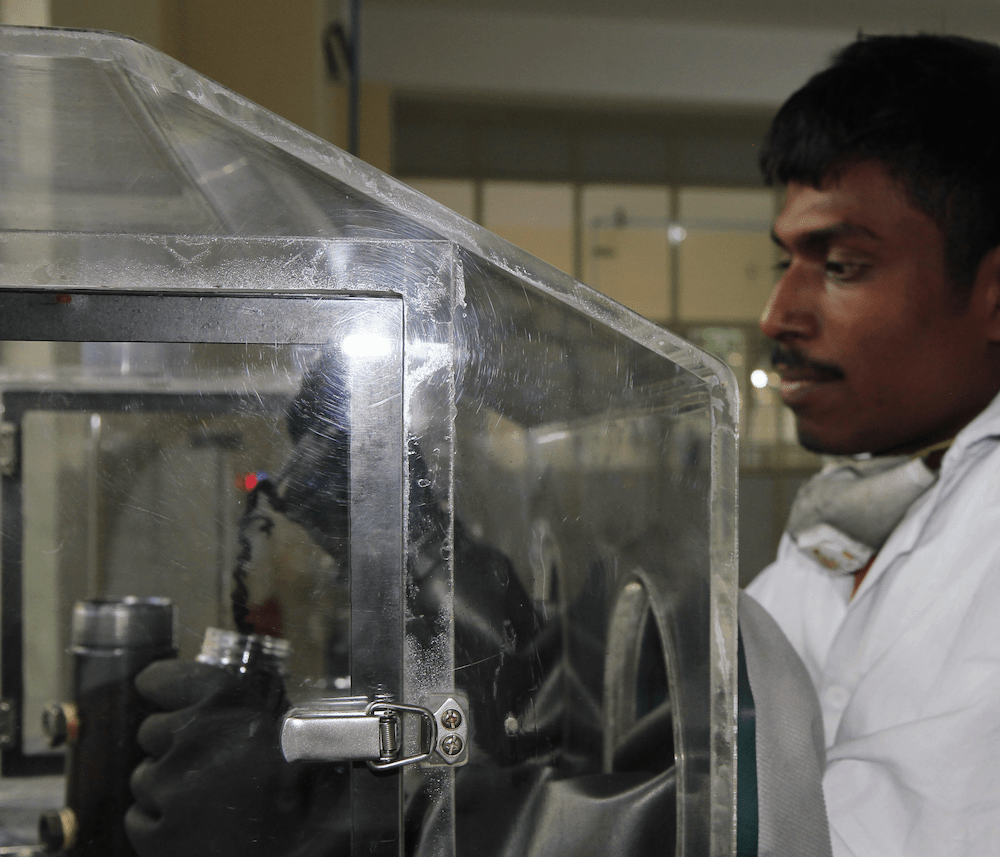
Anto assessing a new batch of Carbon Nanotubes 
Manufacturing vessel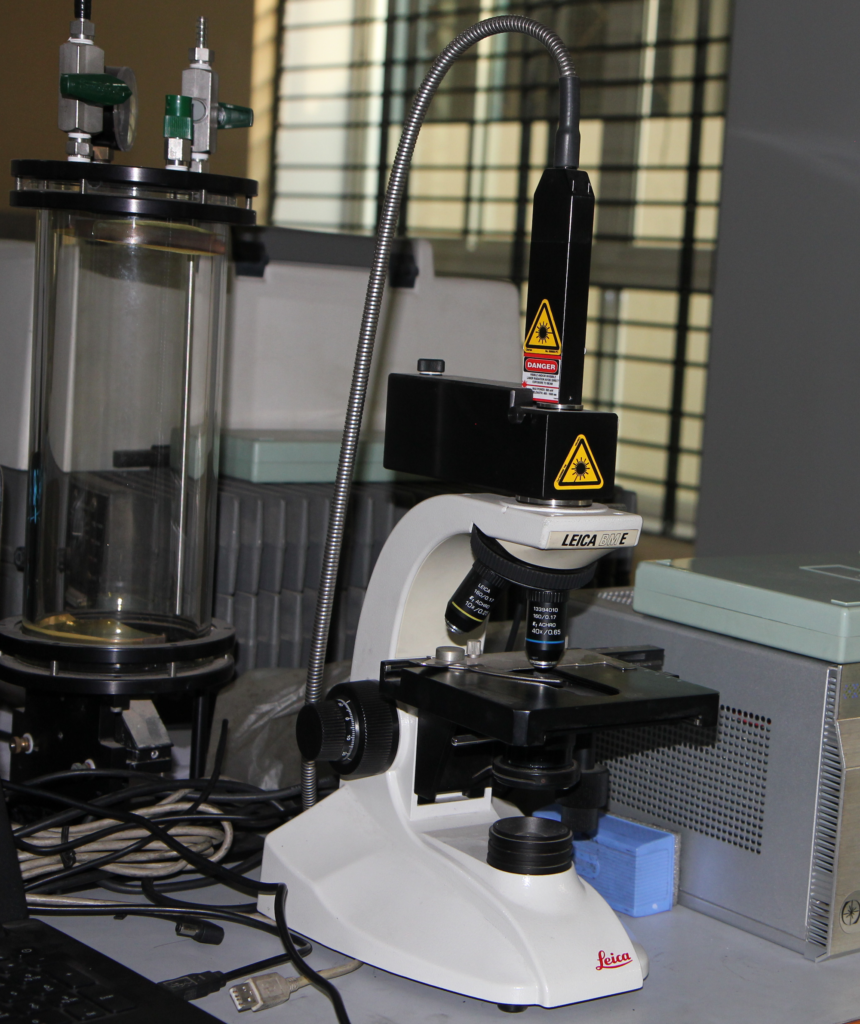 
Raman Specrometer


