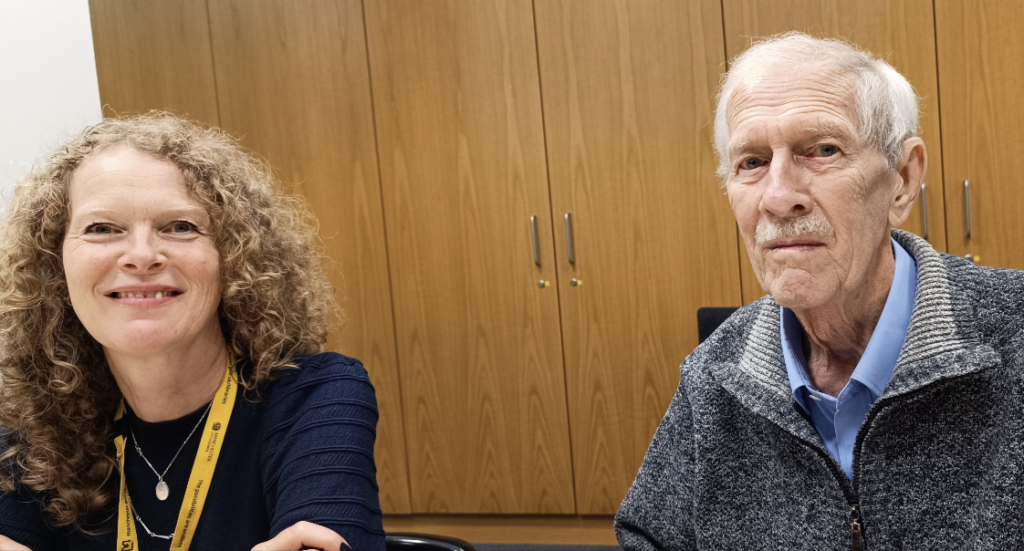
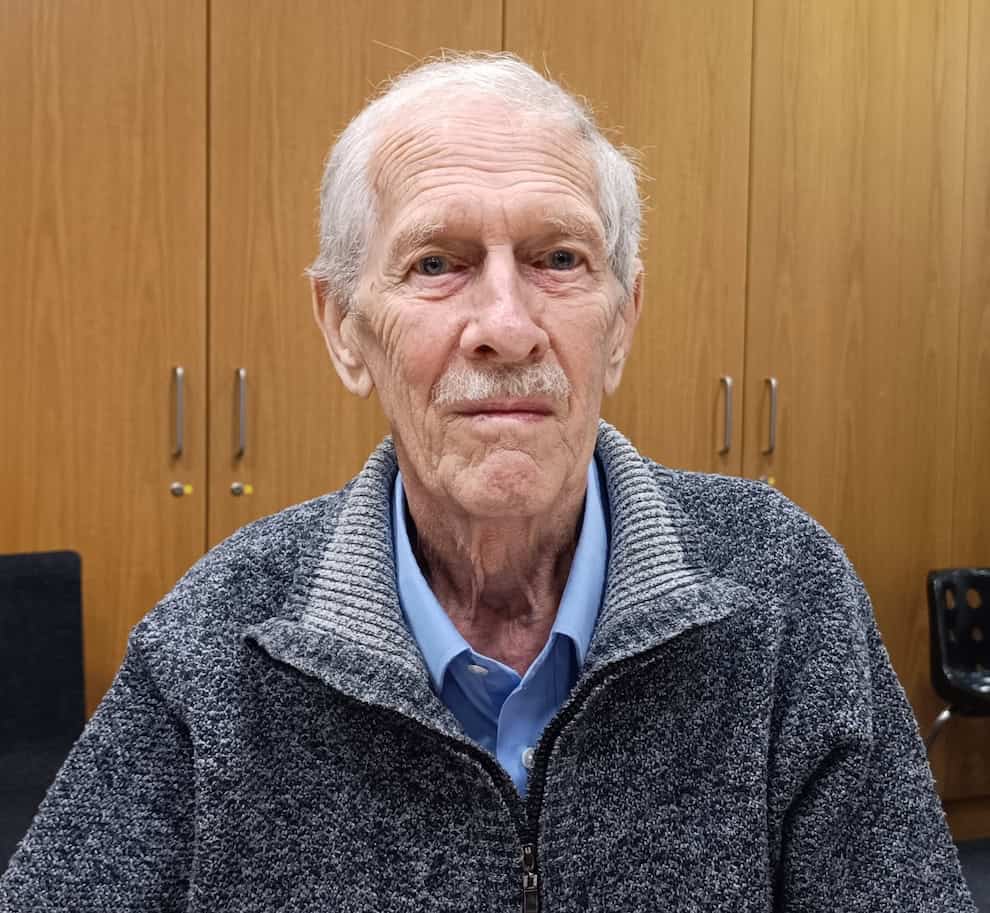
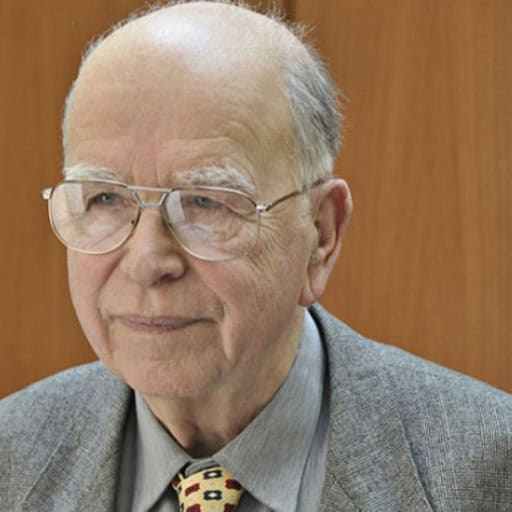
During the International Astronautical Congress in Milan in October 2024, Professor Iván Almár was elected to be a member of the Astronautics Hall of Fame.

It is an honour previously bestowed on individuals or groups that in the past have included Apollo 11 astronauts, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, Zezhou SUN Designer-in-Chief of Chang’e-4 Program, Yuri Koptev General Director of the Russian Space Agency, the James Webb Space Telescope team from (NASA, ESA and CSA), and the Tianwen-1 Spacecraft Development Team.
I am familiar with Theodore Von Karman and Herman Oberth, both of whom are associated with Hungary. They played an instrumental role in the development of astronautics. Since Hungary was under the influence of the USSR for most of the post-WW2 years, the astronautics it conducted were not easily publicly accessible.
Ivan Almar completed his university studies in 1954 and became aware of the activities for the International Geophysical Year 1957-58. He knew that the USSR Academy of Sciences and other countries planned to build and launch satellites to observe the Earth from orbit. The coincidence of time and place set him on his long career. His contributions included
- Director of the Konkoly Observatory in Budapest
- The founding director of the Satellite Geodetic Observatory in Hungary
- President of the Hungarian Astronautical Society
- Co-developer of the Rio Scale, used to quantify the impact of any public announcement regarding evidence of extraterrestrial intelligence.
- Author of the San Marino Scale to quantify the potential impact of employing electromagnetic communications technology to announce Earth’s presence.
- The London Scale can evaluate and present complex information about the scientific importance, validity and potential consequences of an alleged discovery of ET life.
- I met and recorded this interview during the International Astronautical Congress in Milan on Friday, 18th October 2024.
I started by asking him how his interest in astronomy started.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 46:41 — 64.7MB) | Embed
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | Spotify | RSS | More