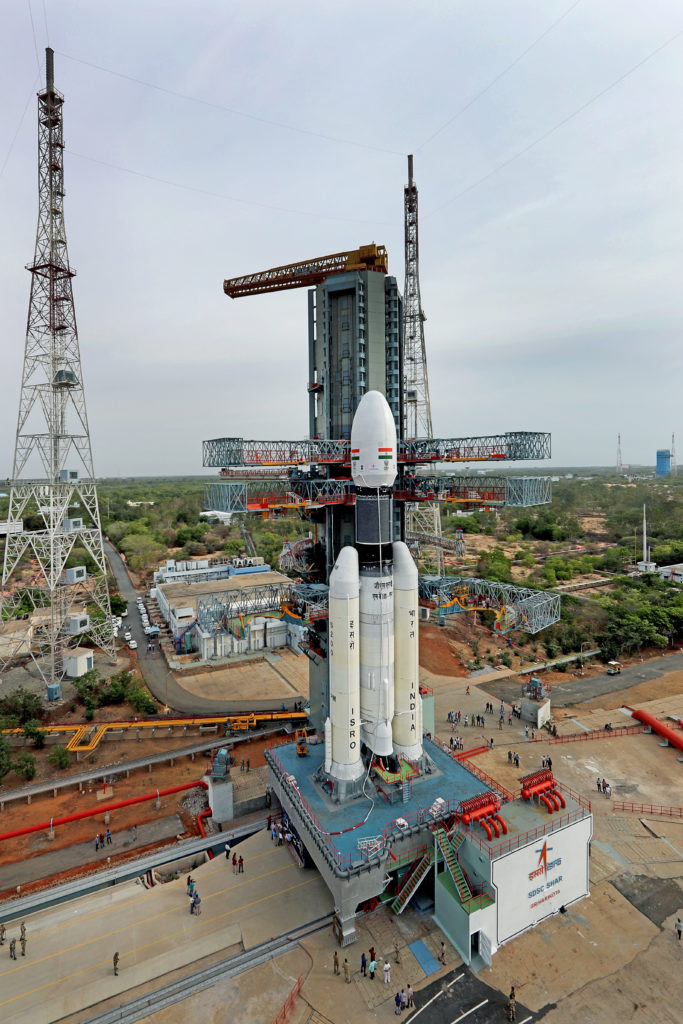
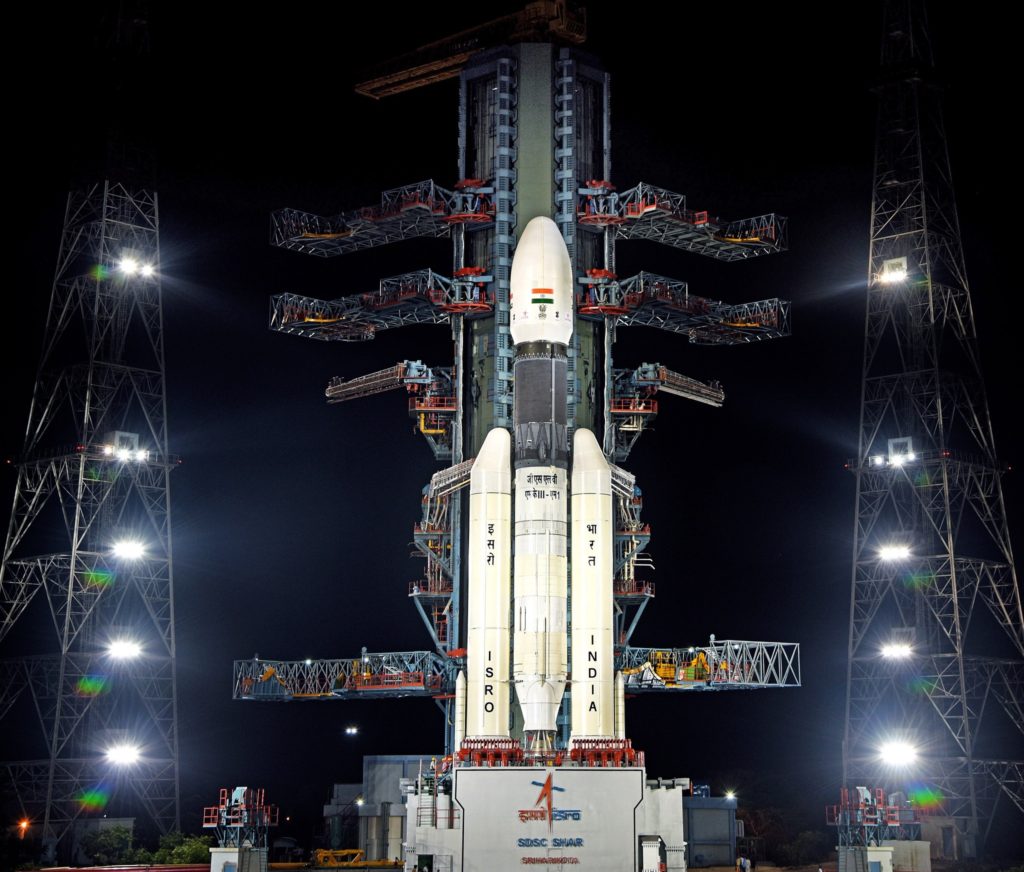
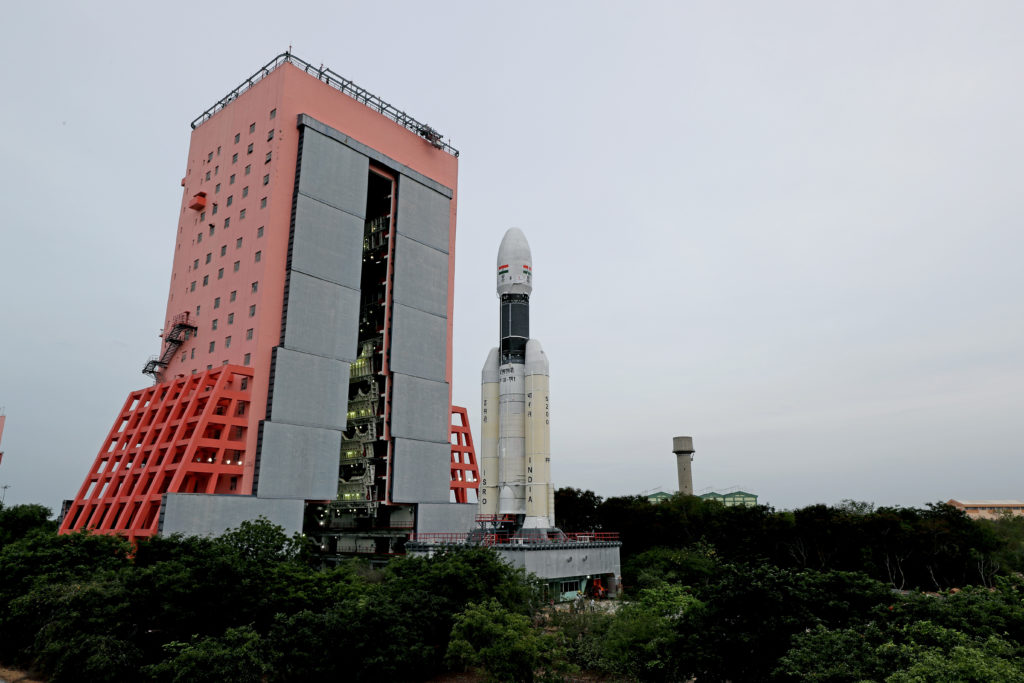
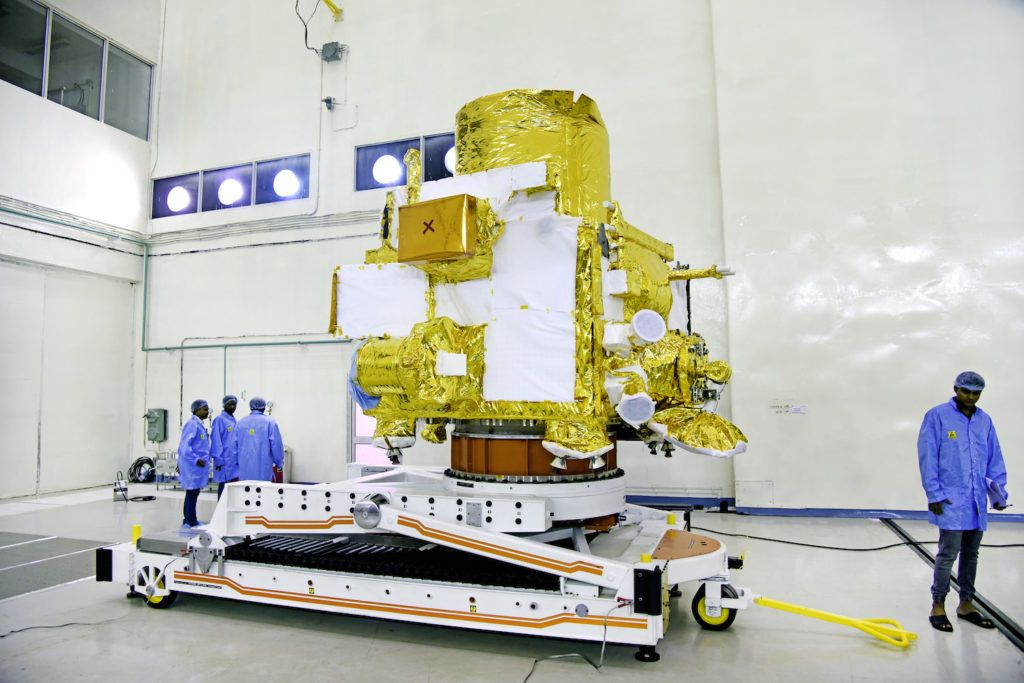
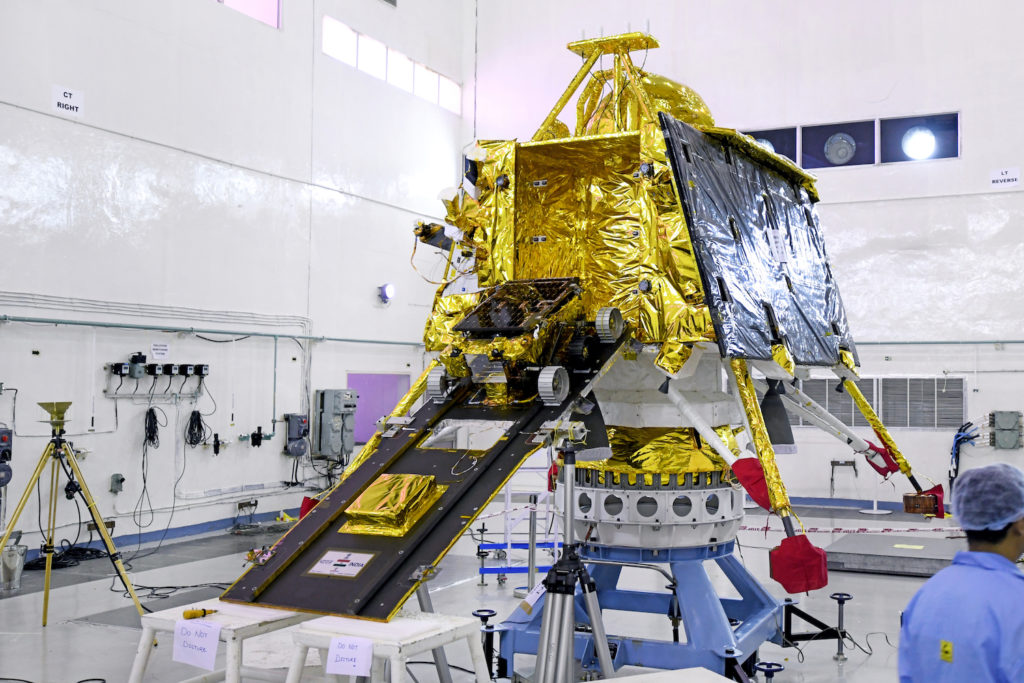
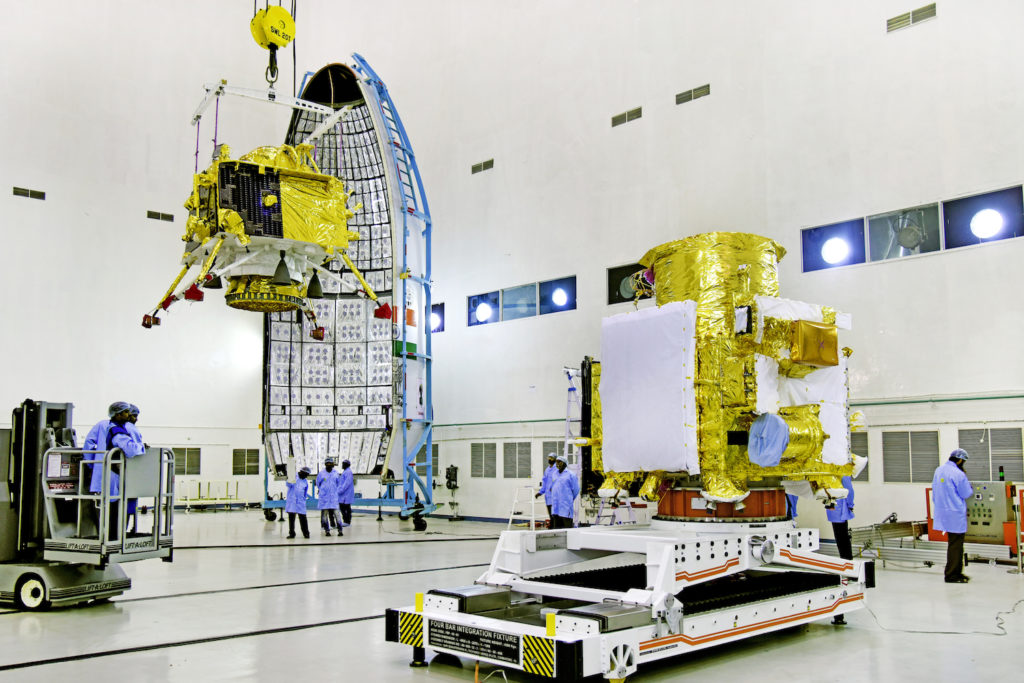
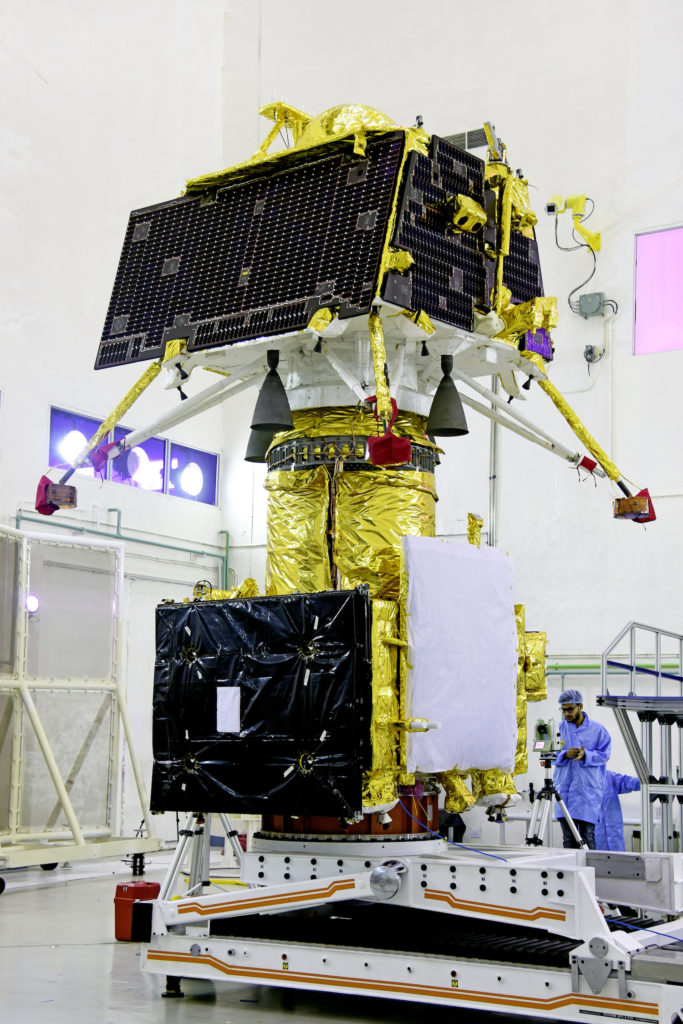
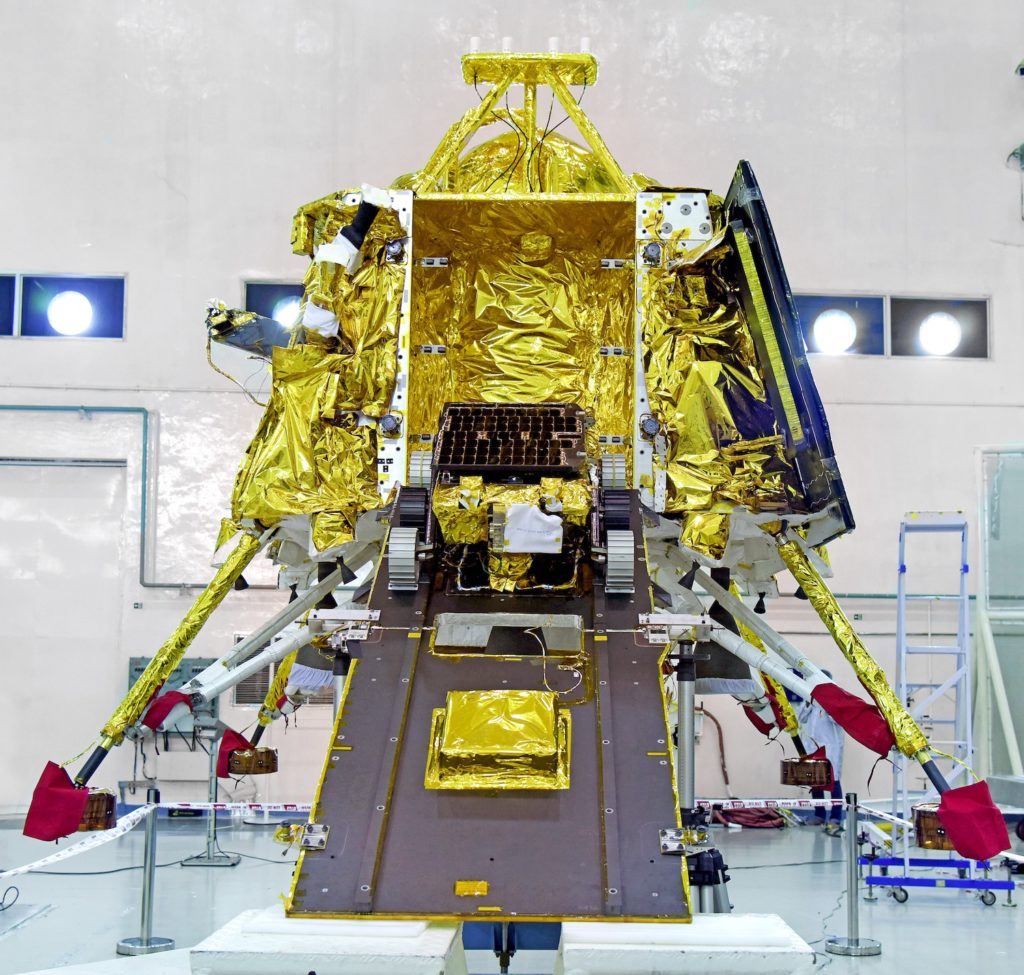
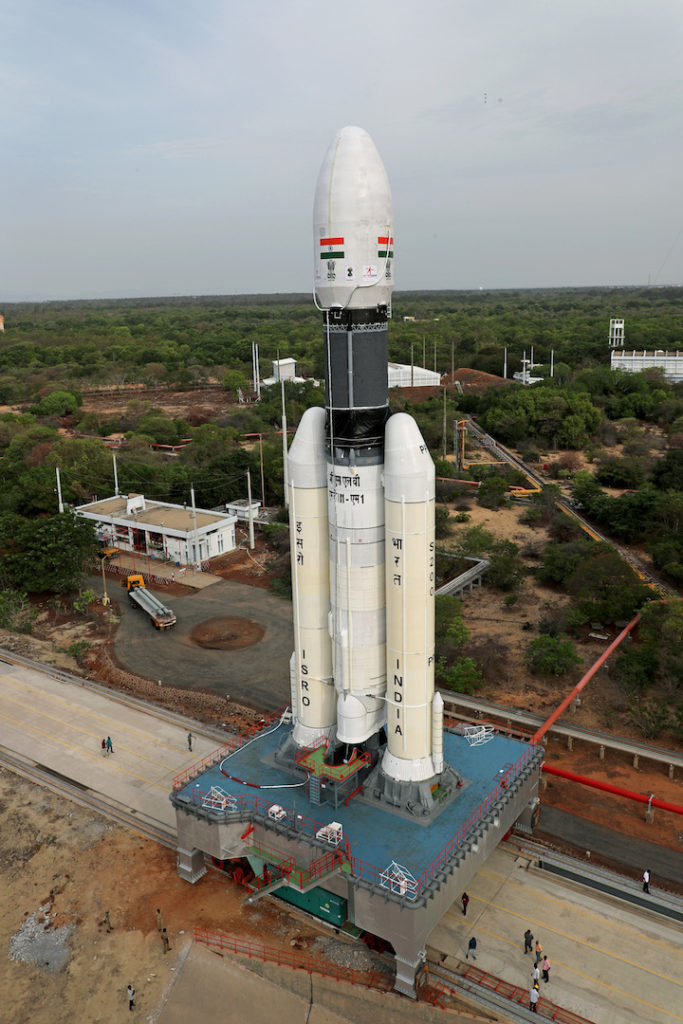
A two-day summit called Spacetronix and Deftronix, organised by the India Electronics and Semiconductor Association in Bangalore attracted over 50 speakers, 45 exhibitors and 600 visitors. The first day, Spacetronics focused on India’s space sector and the second on defence – Deftronix. The key themes addressed the state of manufacturing of hardware, outsourcing and supply chain, a closer look at some successful space startups and the challenges of standards and security.
The two-day event was extremely well organised and the venue, the Taj Yeshwantpur, met all the needs. It was disappointing that the organisers were left waiting by the tardy attendance by the keynote speaker, the first one on the second day. Being an industry centred event, many of the presentations involved major sponsors showcasing their products. Some of the speakers such as minister of state Dr. Jitendra Singh and DRDO chairman Dr. Satheesh Reddy did mot make an appearance but in both cases, their billing was subject to confirmation.
The first day focused on space. Representatives from a variety of Indian Space Research Organisation centres made presentations indicating their willingness to engage with the private sector to help meet their increasing capacity demands in avionics, semiconductors, 4th generation wifi products, digital receivers, high-speed data acquisition and playback, Field Programmable Gate Arrays, systems and cybersecurity. In addition to capacity building and reducing costs, ISRO was looking to the bourgeoning private space sector to introduce innovations in products design and manufacturing techniques.
The general view from outside ISRO is that India’s space sector is dominated by its national space agency – The Indian Space Research Organisation. Private sector startups find it hard to overcome ISRO’s role as the primary producer, customer and regulator. The emerging space startups see ISRO as a gatekeeper restricting the commercial opportunities to new players.

ISRO Semiconductor Laboratory in Punjab
Multinationals choose to setup manufacturing plants in China because, unlike India, China has an internal market for their products. India’s advantage, a cheap labour force, is offset by the need to export goods once they are made in India.
Challenges experienced by the private sector when working with ISRO included
- No single point of contact for initial registration by a private sector company
- No support (risk sharing) for small companies that invest in prototyping as part of the bid-process
- ISRO is a big organisation and currently has no template for interfacing with the private sector.
- Start-ups have to work work to ISRO’s methods and process which are not consistent.
- Companies that work with ISRO IP tend to be favoured over those that are offering independent products and services
The two-day event was supported by an exhibition where national and international companies showcased their products and services. Representatives from ISRO centres made presentations indicating their requirements for specific products and services to assist with capacity, cost or new innovative solutions. Whilst ISRO centres hold international industry standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality), AS9000 (Aerospace) and 14001 (Environment) but security standards such as ISO 27001 was conspicuous by its absence. This was especially striking since security was a major theme of the event.
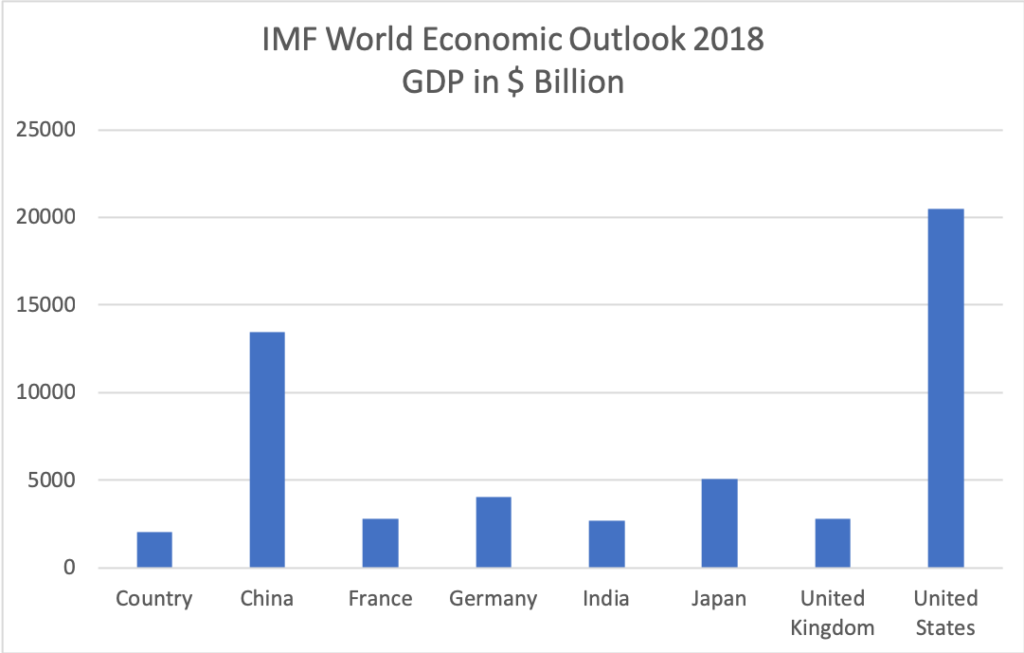
In June 2019, India’s prime minister announced a new target of 5 trillion USD digital economy by 2024 from the current 2.8 trillion USD. Space and defence are two of the sectors where the digital economy will grow. Numerous former ISRO chairmen have announced initiatives to facilitate greater engagement with the private sector but engagement remains weak.
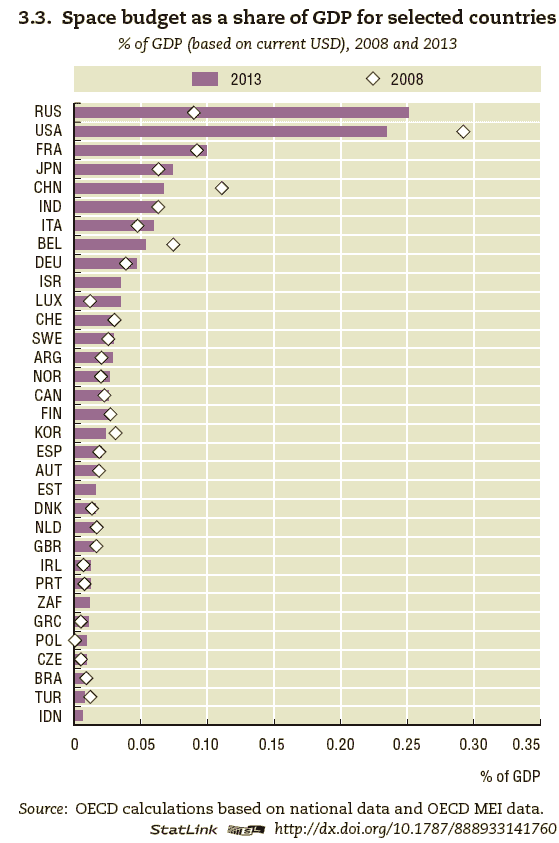
NASA has about as many employees as ISRO but 20 times the budget. Most of NASA’s budget is spent on outsourced projects. Although NASA was not explicitly cited, one theme was to learn from other countries on the benefits of outsourcing space projects. An interesting word used during an ISRO presentation was “Indeginization”. This was a reference to a desire for ISRO to make in-house components and systems that are currently imported or made by international manufacturers in India.
During the early 1990s, India’s went through an economic liberalisation that reduced the role of the government and attracted private and foreign investments. Millions of Indians benefited from easier, cheaper and faster access to private telephone lines, cars and household goods. The national economy has seen huge growth since. For India to achieve similar growth in the new strategic areas of space and defence, a similar liberalisation is required if the targets of the digital economy are to be met. One urgent step for the government is the needs to establish a space policy and publish a space bill that will allow the nascent Indian startups to flourish.