The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) was founded in 2003 through the merger of three existing organisations and has an annual budget of around 2 billion USD. It has a remit for research and development of technology, space exploration and supporting human spaceflight aboard the ISS through collaboration with the European Space Agency. This episode is available in audio and video below.
In 2003, JAXA launched Hayabusa-1 to explore the asteroid Itokawa. It arrived at Itokawa in 2005 and returned to the Earth with a tiny sample in 2010. In 2014, JAXA launched Hayabusa-2 to explore asteroid Ryugu. Hayabusa2 arrived at Ryugu on 27 June 2018 and will remain in Ryugu orbit until 2019. It will collect three discrete samples (between 0.1g and 1g in each case), store them in separate sealed containers on board for return to Earth in December 2020, in the Woomera test range in Australia.
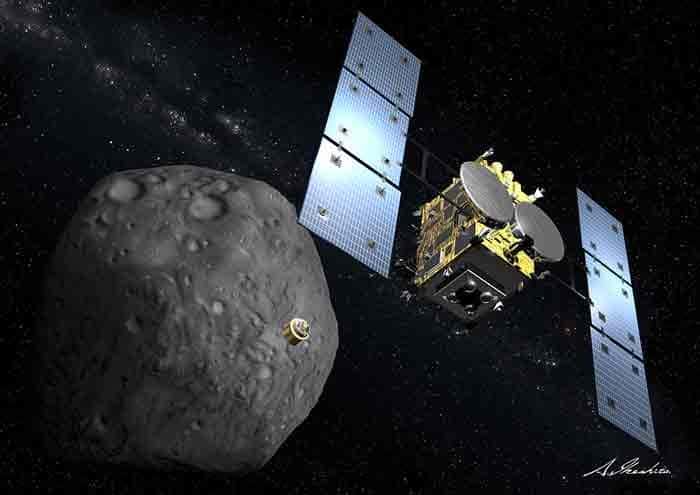
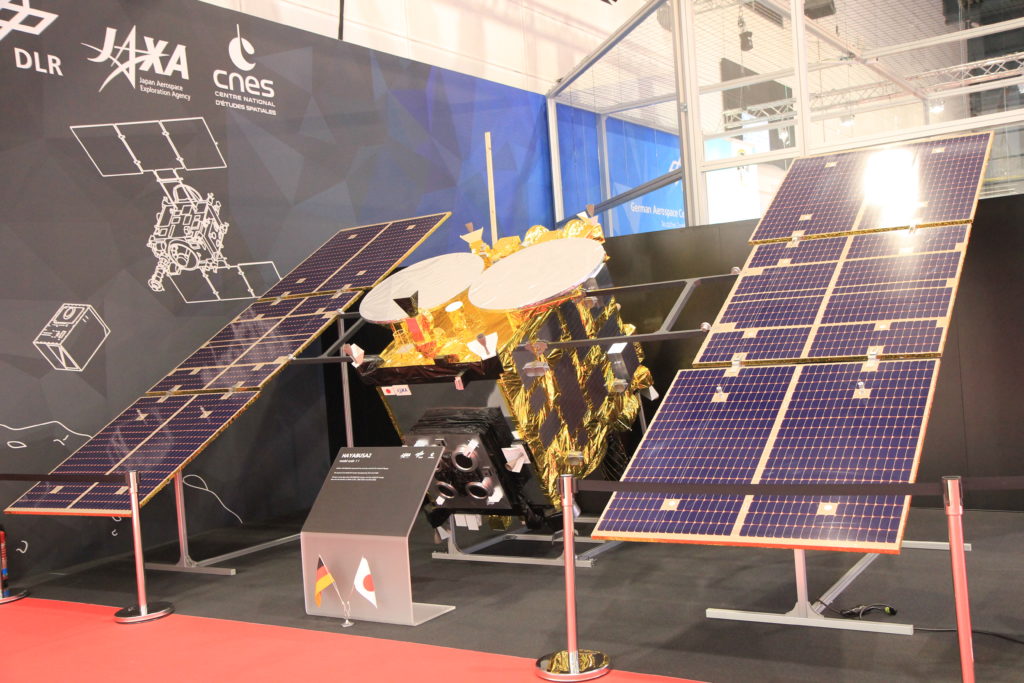
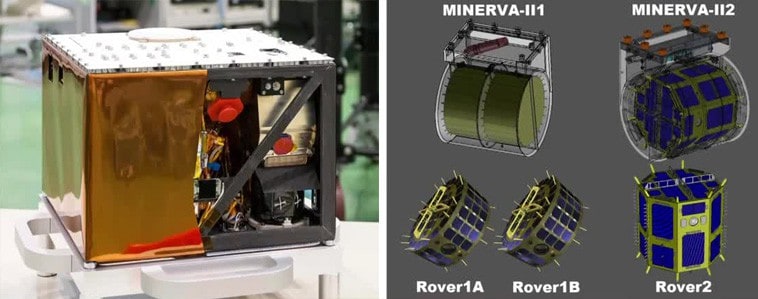


Hyabusa2 has four rovers.
- MINERVA-II-1 contains two rovers, Rover-1A and Rover-1B, which were deployed on 21 September 2018.
- Mascot – a rover developed by the German and French space agencies. Deployed on 3rd October 2018.
- The MINERVA-II-2 contains ROVER-2, a payload developed by several universities in Japan and planned for deployment in July 2019.
JAXA is also considering
- 1 The launch of the world’s smallest lunar lander is intended to be launched on NASA’s Space Launch System in the 2020s.
- Smart Lander for Investigating the Moon (SLIM) will demonstrate precision landing technology.
- Selene-R – a tentative joint JAXA/ISRO Moon mission to soft-land a rover on the Moon. Jaxa would supply the rover, and ISRO would supply the lander.
- MMX – Martian Moons Exploration. A martian sample return mission. Only possible with international collaboration (US, France, Germany). To be launched around 2024. Following a period of 3 years at Mars, it will return to Earth with a sample from Phobos in 2029.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 22:35 — 18.1MB) | Embed
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | Spotify | RSS | More