Christopher Riley was trained as a geologist, but his greatest skill is his imagination. He is known for his books and as a filmmaker, specialising in documentaries including In the Shadow of the Moon, First Orbit (on Youtube) and Director’s Cut of Moonwalk One (Amazon DVD)
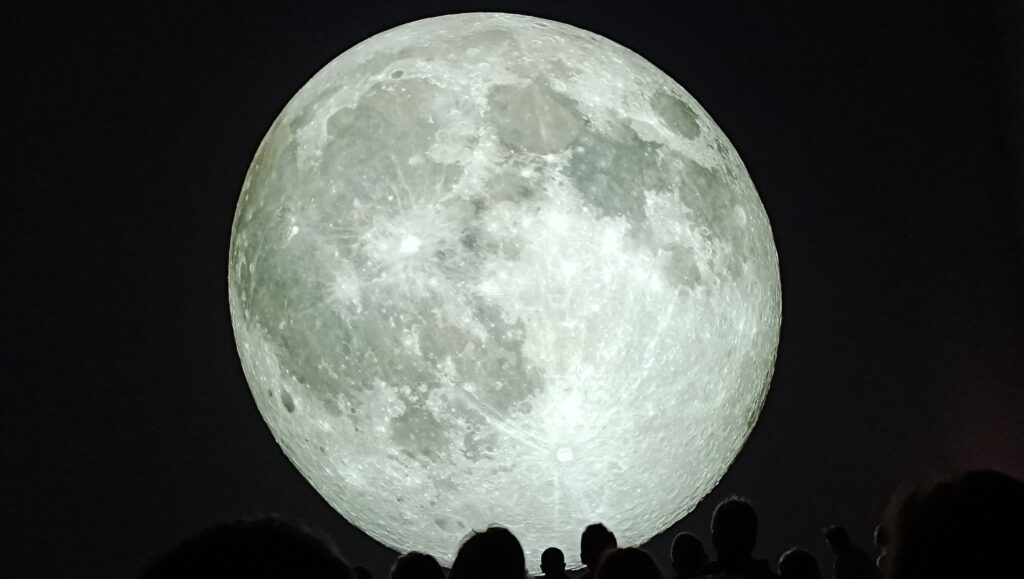
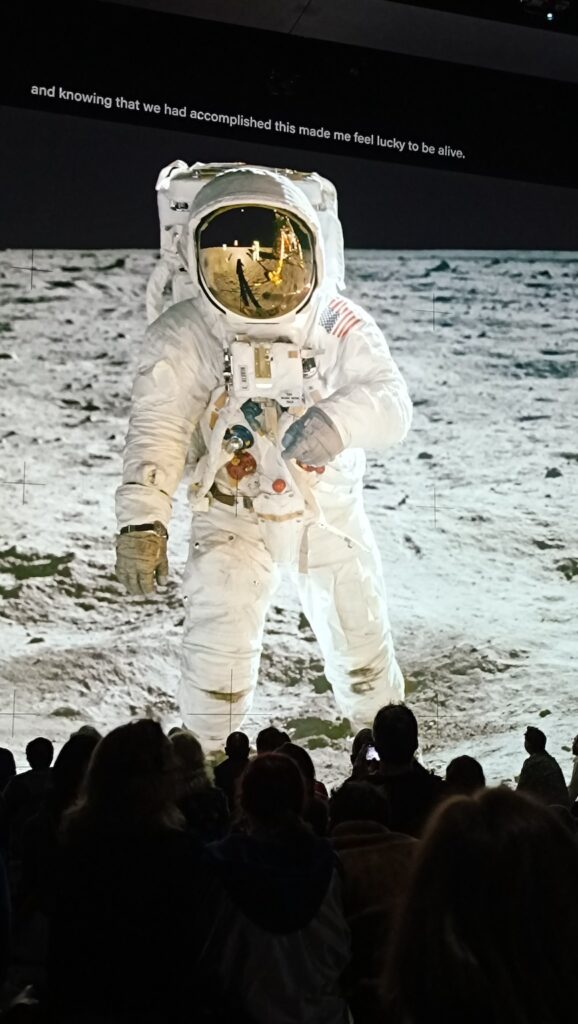
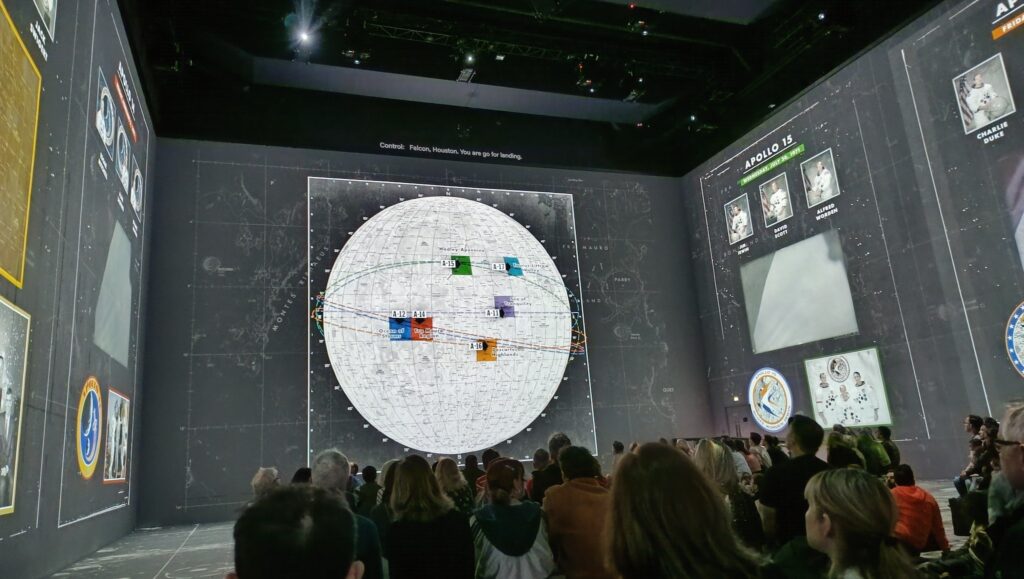
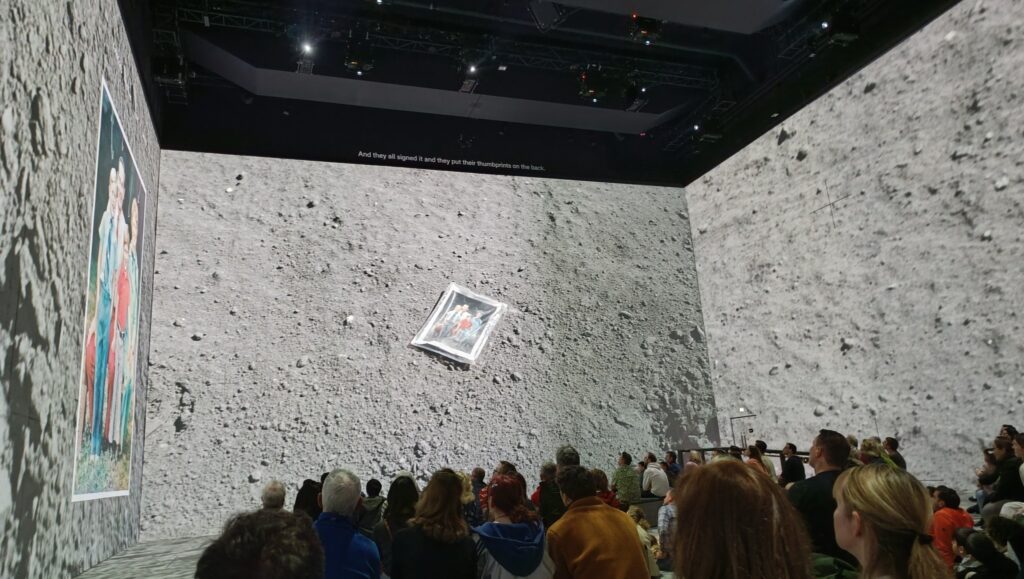
His latest work, a 50-minute show, The Moonwalkers: A Journey with Tom Hanks is an immersive audio-visual experience in a unique venue in the centre of London. The visuals are provided by 26 high-res Panasonic laser projectors that produce giant videos and still images that wraps around multiple walls. The exceptional audio is powered by the German-made Holoplot speaker system comprising 1600 speakers. If you ever wondered what comes after Imax – this is it.
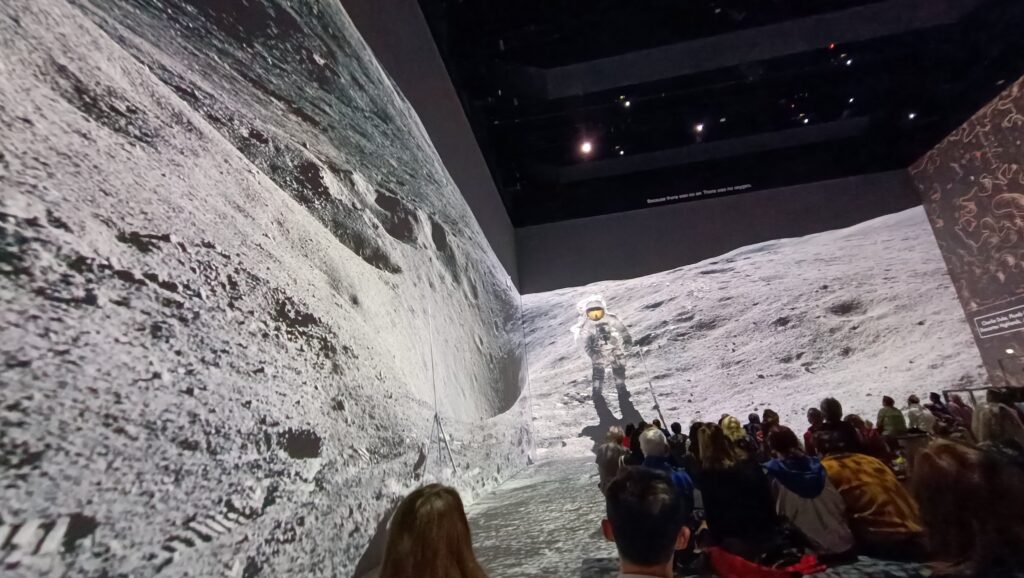

The script was written by Tom Hanks and Christopher Riley. This unique audio-visual experience of the Apollo story is available only in London and only until 13th October 2024. More images and clips here.
The Space Race, that started with Gagarin’s spaceflight on April 1961 and arguably ended in July 1969 with Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin walking on the surface of the Moon. It is perhaps the most astonishing episode of human progress. It was an epic leap because it was more than just a technological advance. It may have been borne out of national rivalries but its legacy touched our individual perceptions of each other on earth and beyond. .
In this conversation, recorded in London he talks about his writing, filmmaking and how the idea of The Moonwalkers came about. Parts of this interview were transmitted in my bi-weekly radio program on allfm.org on 28th May 2024.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 56:30 — 103.5MB) | Embed
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | Spotify | RSS | More